Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract▲ | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
11 Dec 2023
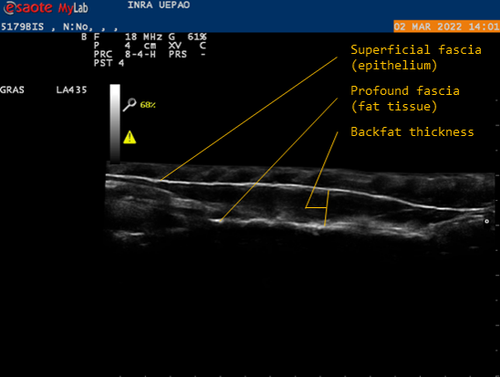
Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotypingNicolas Bédère, Joëlle Dupont, Yannick Baumard, Christophe Staub, David Gourichon, Frédéric Elleboudt, Pascale Le Roy, Tatiana Zerjal https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04172576Towards a better optimization of the genetic improvement of chicken breeds: Introduction of simple phenotypic traits related to body composition for easy measurement in the selection programs of laying hens.Recommended by Seyed Abbas Rafat based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In genetic selection, simplistic model of single-trait selection is usually considered, and the response to such approach is estimated using simple models. In practice, however, plant and animal breeders always deal with the selection of several traits, hence making the selection process very complex. Therefore, the simultaneous genetic improvement of several traits has always been one of the goals of livestock, including poultry breeding (Falconer, 1972). Studies that examine the indirect effects of selection on economic traits are eagerly awaited. In this context, the results of the study by Bédère et al., (2023) gives new insights about phenotypic and genotypic relationships between body reserves traits in laying hens. The authors aimed to propose novel data about the genetic architecture of traits related to body fat by measuring a series of phenotypic traits with relatively an easy approach. The authors further aimed to test and validate the phenotyping of backfat thickness as an indicator of the overall fatness of laying hens. Thus, the study allowed providing new evidence regarding the genetic determination of the backfat trait in chicken breeds. The authors first estimated the effect of selection on the residual feed intake (trait x) on the trait of body reserves (trait y). In fact, divergent selection experiments are a fundamental research tool that allow revealing significant amount of data related to the possible span of genetic improvement for traits of interest. Consequently, by analyzing data from a divergent selection experiment, associations have been estimated between a number of feed-dependent traits that have practical use for chicken breeders. Estimation of the correlations between traits is under question in terms of the theory of genetics and their application in multi-trait selection. As a major finding of the study, the observation of a bimodal distribution of backfat in both lines and the heterogeneity of the variances between families allowed suggesting a possible major gene, which could be investigated in future studies using for instance quantitative genetics. Body composition is continually studied in broilers chicken, but this aspect of chicken genetic is more detailed in laying hens. The current findings are worthy to validate using several approaches. In fact, one of the limitations of the study can be related to other statistical models that can be built. For example, the study revealed high correlations between egg production and body weight, thus body weight could be considered as a covariate in regression models. Moreover, the principal trait of selection (based on the residual feed intake) could be considered. References: Falconer, D. S. (1972). Introduction to Quantitative Genetics. Publisher: Ronald Press Company. pp 365. Bédère, N., Dupont, J., Baumard, Y., Staub, C., Gourichon, D., Elleboudt, F., Le Roy, P., Zerjal, T. (2023). Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotyping. HAL ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04172576 | Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotyping | Nicolas Bédère, Joëlle Dupont, Yannick Baumard, Christophe Staub, David Gourichon, Frédéric Elleboudt, Pascale Le Roy, Tatiana Zerjal | <p>In this study, we pursued three primary objectives: firstly to test and validate the phenotyping of backfat thickness as an indicator of the overall fatness of laying hens; secondly, to estimate genetic parameters for this trait; thirdly, to st... |  | Animal genetics, Poultry, Statistical genetics | Seyed Abbas Rafat | 2023-07-27 17:09:10 | View | |
14 Dec 2022
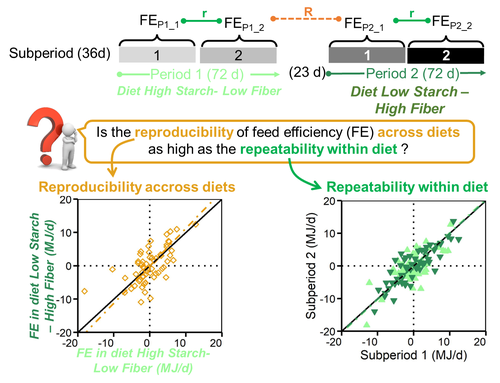
Feed efficiency of lactating Holstein cows was not as repeatable across diets as within diet over subsequent lactation stagesAmelie Fischer, Philippe Gasnier, philippe faverdin https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.10.430560A focus on feed efficiency reproducibility and repeatability of dairy cows fed different diets over the lactation stage.Recommended by Alberto Atzori based on reviews by Ioannis Kaimakamis, Angela Schwarm and 2 anonymous reviewersThe topic of feed efficiency is under discussion in the scientific community and several studies pointed out that lactation stage has to be accounted for when estimates of feed efficiency are carried out, especially for genetic ranking of animals and their performances, as highlighted by Li et al. (2017). Other researchers applied a latin square design to test dietary effects across lactation (Ipharraguerre et al. 2002) but this approach cannot be followed out of experimental conditions and particularly does not allow, nowadays, to valorize precision livestock farm data to get phenotypic information from individual animals at farm level. The current manuscript by Fischer, et al. (2022a) describes an experimental trial in which cows were first fed a high starch diet-low fibre then switched over to a low starch diet-high fibre and individually monitored over time. Data were analyzed with the objective to investigate effects within diets and across diets. Since all cows went through the same sequence at the same time it was not possible to completely separate the confounding effect of lactation stage and diet as stated by the authors. However, this manuscript adds methodological discussions and opens research questions especially to the matter of repeatability and reproducibility of feed efficiency of individual animals over the lactation stage. These variables are fundamental to evaluate nutritional traits and phenotypic performances of dairy cows at farm level, as highlighted by a paper of the same first author (Fischer, et al. 2022b) dealing to reproducibility and repeatability with a similar approach. My opinion is that this manuscript gives the opportunity to enlarge the scientific discussions on the calculation of repeatability and reproducibility of feed efficiency of individual animals over time. In particular, as in this study, specific mathematical approaches need to be carried out with the final goal to analyze and valorize precision livestock farm data for cow phenotyping and to propose new methods of feed efficiency evaluations. It also needs complete databases carried out under experimental conditions. In fact it has to be considered that this manuscript makes available to the scientific community all the data and the R code developed for data analysis giving the opportunity to replicate the calculations and propose new advancements in the feed efficiency evaluations of dairy cows. References Fischer A, Gasnier P, Faverdin P (2022a) Feed efficiency of lactating Holstein cows was not as repeatable across diets as within diet over subsequent lactation stages. bioRxiv, 2021.02.10.430560, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.10.430560 Fischer A, Dai X, Kalscheur KF (2022b) Feed efficiency of lactating Holstein cows is repeatable within diet but less reproducible when changing dietary starch and forage concentrations. animal, 16, 100599. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ANIMAL.2022.100599 Ipharraguerre IR, Ipharraguerre RR, Clark JH (2002) Performance of Lactating Dairy Cows Fed Varying Amounts of Soyhulls as a Replacement for Corn Grain. Journal of Dairy Science, 85, 2905–2912. https://doi.org/10.3168/JDS.S0022-0302(02)74378-6 Li B, Berglund B, Fikse WF, Lassen J, Lidauer MH, Mäntysaari P, Løvendahl P (2017) Neglect of lactation stage leads to naive assessment of residual feed intake in dairy cattle. Journal of Dairy Science, 100, 9076–9084. https://doi.org/10.3168/JDS.2017-12775
| Feed efficiency of lactating Holstein cows was not as repeatable across diets as within diet over subsequent lactation stages | Amelie Fischer, Philippe Gasnier, philippe faverdin | <p> Background: Improving feed efficiency has become a common target for dairy farmers to<br>meet the requirement of producing more milk with fewer resources. To improve feed<br>efficiency, a prerequisite is to ensure that the cows identified... |  | Cattle production, Ruminant nutrition | Alberto Atzori | Anonymous, Ioannis Kaimakamis, Giuseppe Conte, Angela Schwarm | 2021-02-11 08:43:59 | View |
05 Jul 2022
Impact of pre-breeding feeding practices on rabbit mammary gland development at mid-pregnancy.Cathy Hue-Beauvais, Karine Bebin, Raphael Robert, Delphine Gardan-Salmon, Mickael Maupin, Nicolas Brun, Etienne Aujean, Florence Jaffrezic, Steve Simon, Madia Charlier, Fabienne Le Provost https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.17.476562Managing the feeding of rabbits to improve metabolic efficiencyRecommended by Giuseppe Conte based on reviews by Marion Boutinaud, Davi Savietto and 1 anonymous reviewerA correct execution of feeding plan for growing rabbit decreases the possibility of post-weaning digestive disorders, thus enhancing the feed efficiency in the animals. However, a limitation of feed daily quantity is required between 10 weeks of age and the first artificial insemination. This limitation causes energy deficiency with a consequent reduction in fertility. Beauvais et al. (2022) studied the impact of feed restriction strategies in female rabbits. Four feed restriction strategies were applied in two distinct periods (post-weaning and puberty) and evaluated by different physiological parameters (growth rate, metabolic profiles, reproductive parameters and mammary gland development). In the first part of the paper, the authors evaluated the association between weight slopes and feeding strategies in the late post-weaning and peripartum period in the four groups. As revealed by the authors, a significant difference was observed during the late post-weaning period, which remained significant between the pubertal and fattening phases. Probably these differences are related to the restriction feeding pattern. The results indicated that restrictive feeding changes in the first step of post-weaning period is associated with a significant difference in body weight. This difference occurs from the third week of diet, highlighting the high sensitivity of growing rabbit to nutrition during the post-weaning period. In the second part of the paper, the authors evaluated the expression of genes involved in the lipid metabolism. During the mid-pregnancy, was revealed a significant higher expression of lipogenic genes, which may be considered as useful markers for the mammary epithelial development in less restrictive strategies during early life period. The results proposed by Beauvais et al. (2022) enlighten the important role played by the feeding conditions of young female rabbits in the early life rearing. In particular, this activity provides specific recommendations for optimizing lactation and thus preventing neonatal mortality of the offspring. Moreover, the authors provide indications about the effect of feeding strategies on the mammary development and gene expression with absolute consequences on the development of offspring. Mammary lipid metabolism affects the milk profile and therefore the growth performance of the young animals. Reference
Hue-Beauvais C, Bebin K, Robert R, Gardan-Salmon D, Maupin M, Brun N, Aujean E, Jaffrezic F, Simon S, Charlier M, Le Provost F (2022). Impact of pre-breeding feeding practices on rabbit mammary gland development at mid-pregnancy. biorXiv, 2022.01.17.476562, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.17.476562 | Impact of pre-breeding feeding practices on rabbit mammary gland development at mid-pregnancy. | Cathy Hue-Beauvais, Karine Bebin, Raphael Robert, Delphine Gardan-Salmon, Mickael Maupin, Nicolas Brun, Etienne Aujean, Florence Jaffrezic, Steve Simon, Madia Charlier, Fabienne Le Provost | <p>Optimizing rabbit does preparation during early life to improve reproductive potential is a major challenge for breeders. Does selected for reproduction have specific nutritional needs, which may not be supplied with the common practice of feed... |  | Animal nutrition modelling | Giuseppe Conte | 2022-01-19 14:44:30 | View | |
09 Apr 2022
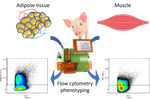
The impact of housing conditions on porcine mesenchymal stromal/stem cell populations differ between adipose tissue and skeletal muscleAudrey Quéméner, Frédéric Dessauge, Marie-Hélène Perruchot, Nathalie Le Floc’h, Isabelle Louveau https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.08.447546Housing conditions affect cell populations in adipose and muscle tissues of pigsRecommended by Hervé Acloque based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThe adaptability of livestock to changing environments is based in particular on their genetic characteristics but also on the farming conditions to which they are subjected. However, this last point is poorly documented and little is known about its contribution to environmental challenges. The study by Quéméner and colleagues [1] addresses this question by assessing the effect of two hygiene conditions (good vs poor) on the distribution of cell populations present in adipose and muscle tissues of pigs divergently selected for feed efficiency [2]. The working hypothesis is that degraded housing conditions would be at the origin of an hyper stimulation of the immune system that can influence the homeostasis of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle and consequently modulate the cellular content of these tissues. Cellular compositions are thus interesting intermediate phenotypes for quantifying complex traits. The study uses pigs divergently selected for residual feed intake (RFI+ and RFI-) to assess whether there is a genetic effect associated with the observed phenotypes. The study characterized different stromal cell populations based on the expression of surface markers: CD45 to separate hematopoietic lineages and markers associated with the stem properties of mesenchymal cells: CD56, CD34, CD38 and CD140a. The authors observed that certain subpopulations are differentially enriched according to the hygiene condition (good vs poor) in adipose and skeletal tissue (CD45-CD56-) sometimes with an associated (genetic) lineage effect. This pioneering study validates a number of tools for characterizing cell subpopulations present in porcine adipose and muscle tissue. It confirms that housing conditions can have an effect on intermediate phenotypes such as intra-tissue cell populations. This pioneering work will pave the way to better understand the effects of livestock systems on tissue biology and animal phenotypes and to characterize the nature and function of progenitor cells present in muscle and adipose tissue. [1] Quéméner A, Dessauge F, Perruchot MH, Le Floc’h N, Louveau I. 2022. The impact of housing conditions on porcine mesenchymal stromal/stem cell populations differ between adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. bioRxiv 2021.06.08.447546, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.08.447546 [2] Gilbert H, Bidanel J-P, Gruand J, Caritez J-C, Billon Y, Guillouet P, Lagant H, Noblet J, Sellier P. 2007. Genetic parameters for residual feed intake in growing pigs, with emphasis on genetic relationships with carcass and meat quality traits. Journal of Animal Science 85:3182–3188. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2006-590. | The impact of housing conditions on porcine mesenchymal stromal/stem cell populations differ between adipose tissue and skeletal muscle | Audrey Quéméner, Frédéric Dessauge, Marie-Hélène Perruchot, Nathalie Le Floc’h, Isabelle Louveau | <p><strong>Background.</strong> In pigs, the ratio between lean mass and fat mass in the carcass determines production efficiency and is strongly influenced by the number and size of cells in tissues. During growth, the increase in the number of c... |  | Monogastrics, Physiology, Veterinary science | Hervé Acloque | 2021-06-08 17:34:54 | View | |
15 Dec 2020
Accuracy of predicting chemical body composition of growing pigs using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometryClaudia Kasper, Patrick Schlegel, Isabel Ruiz-Ascacibar, Peter Stoll, Giuseppe Bee https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.15.286153Accurate predictions of chemical composition of pigs for a wide range of body weights: no longer a myth!Recommended by Florence Gondret based on reviews by Mathieu Monziols and 1 anonymous reviewerAssessing body or carcass composition in growing pigs is essential to refine nutritional models, select for specific traits and evaluate pork products. The gold standard methods are dissection and chemical measurements, which are time-consuming and invasive ways to obtain the data. Different teams have tested dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), especially for determining total and regional body composition of fat, soft lean tissues and bone minerals [1-3]. The DEXA measurements are quick, non-invasive, precise, and operator independent. However, the instruments from different manufacturers are unique in implementation so that it is difficult to obtain and share generalized equations. In addition, the validity and accuracy of the measures when applied to pigs having very different composition have been scarcely addressed.
The present manuscript shows that carcass analysis by DEXA can be used to predict empty body chemical composition, and it provides accuracy values for the content in single nutrients (protein, lipids, Ca, P). The body weight range used to generate differences in body composition is very large (20 to 100 kg), which is important when studying pigs along growth. Moreover, regression equations within weight classes (20, 60 and 100 kg) show no important biases, with the exception for body fat especially at the earliest growth stages. Limitations of the technique are the needs of anesthesia when applied to living pigs, and of standardizing the positions of body, carcass and cuts when applied to living or dissected pigs. Another originality of the manuscript is the comparison of the obtained calibrations with previously published prediction models, showing that the differences do not preclude the possibility to use a single model when built from a meta-analysis of the different data. Taken together, this work offers good perspectives to refine nutritional models by inputs from rapidly analyzed body chemical composition and to monitor body and carcass composition in several pigs for genetics applications.
References [1] Mitchell AD., Scholz AM., Pursel VG., and Evock-Clover CM. (1998). Composition analysis of pork carcasses by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Journal of Animal Science. 76(8), 2104-14. https://doi.org/10.2527/1998.7682104x [2] Marcoux M., Bernier JF., and Pomar C. (2003). Estimation of Canadian and European lean yields and composition of pig carcasses by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Meat Science. 63(3), 359-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1740(02)00094-3 [3] Kipper M., Marcoux M., Andretta I., and Pomar C. (2018). Repeatability and reproducibility of measurements obtained by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry on pig carcasses. Journal of Animal Science, 96(5), 2027-2037. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skx046 " | Accuracy of predicting chemical body composition of growing pigs using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry | Claudia Kasper, Patrick Schlegel, Isabel Ruiz-Ascacibar, Peter Stoll, Giuseppe Bee | <p>Studies in animal science assessing nutrient and energy efficiency or determining nutrient requirements necessitate gathering exact measurements of body composition or body nutrient contents. Wet chemical analysis methods or standardized dissec... |  | Agricultural sustainability, Animal nutrition modelling, Monogastrics, Physiology, Pig nutrition | Florence Gondret | 2020-09-17 10:44:58 | View | |
24 Mar 2023
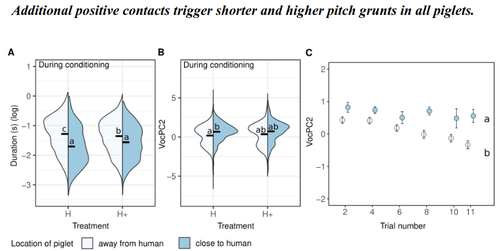
The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationshipAvelyne S Villain, Carole Guérin, Céline Tallet https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.15.484457Qualitative aspects of grunts vary with pigs' mental statesRecommended by Isabelle Veissier based on reviews by Matteo Chincarini and 1 anonymous reviewerVillain et al., (2023) investigated the structure of vocalisations in piglets in relation to human-animal-relationship. They first established a positive relationship by habituating piglets to be positively handled at weaning or later on after weaning. They then compared the reactions of piglets previously positively handled at weaning to that of non-handled piglets during tests in presence of a human (interacting or not), and also before and after the conditioning period when all piglets received positive contacts. They showed that the duration and frequency of grunts emitted in the presence of the human depends on previous contacts. More specifically, grunts are shorter and higher pitched in pigs that have been positively handled, in line with a positive human-animal relationship which is also observed through proximity of the piglets with the human. The authors concluded that the structure of pig vocalisation can reflect the quality of their relationship with humans. The authors also showed that not only the response to humans is modified by positive contacts but also the general mood of piglets, with piglets positively handled at weaning emitting shorter grunts than non-handled piglets, whatever the context. Another interesting finding is the temporality of behaviour of pigs habituated to positive contacts: during the first tests, they stay close to the human, probably being reassured by the proximity of the human. Then, when tests are repeated, they explore more the test room, using the human as an exploratory basis as already reported in the literature. The hypotheses of the study are clear. The methods are reported in details so that the work is reproducible. The interpretation of results is sound. The manuscript is clearly written. This paper brings new and original knowledge in the field of animals’ emotional responses and human-animal relationship: on the structure of grunts in relation to positive affects (positive emotion, positive mood) and on the temporality of the responses to human presence. I recommend this manuscript for its originality and quality. Isabelle Veissier Villain, A.S., Guérin, C., Tallet, C., 2023. The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationship. bioRxiv 2022.03.15.484457, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.15.484457 | The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationship | Avelyne S Villain, Carole Guérin, Céline Tallet | <p>Studying human-animal interactions in domestic species and how they affect the establishment of a positive Human-Animal Relationship (HAR) may help us improve animal welfare and better understand the evolution of interspecific interactions asso... |  | Animal behaviour , Animal cognition, Animal welfare | Isabelle Veissier | 2022-03-23 09:34:45 | View | |
27 Jul 2023
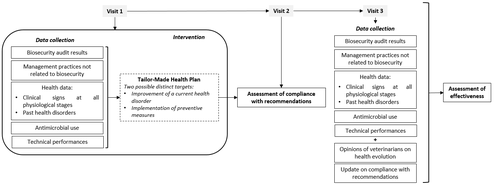
Combining several indicators to assess the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans in pig farmsLevallois Pierre, Leblanc-Maridor Mily, Scollo Annalisa, Ferrari Paolo, Belloc Catherine, Fourichon Christine https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7789634Evaluating tailor-made health plans in pig farms: a multiple complementary indicators approachRecommended by Matteo Chincarini based on reviews by Carla Gomes and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Carla Gomes and 1 anonymous reviewer
Tailor-made health plans for farming animals, including pigs, are highly beneficial due to their customized nature, addressing the unique needs of each farm and promoting efficient husbandry practices. However, assessing the effectiveness of individualized approaches can be challenging. Levallois et al. (1) tackled this challenge by evaluating the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans of pig farms based on a systematic biosecurity and herd health audit. The study involved twenty farrow-to-finish pig farms, each receiving specific plans tailored to their specific needs. Compliance with the recommendations was monitored over an eight-month period. In the literature, various studies have delved into specific issues in detail, such as disease incidence (e.g., (2)). However, the authors of this research applied a comprehensive approach through an integrative analysis of multiple complementary indicators to provide an effective evaluation of the changes and health disorders. The authors' holistic approach to measuring the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans is noteworthy. They employed up to seven methods to identify advantages and limitations, providing valuable insights for applied research and practitioners in the field of farm animals. Additionally, the study's inclusion of diverse farms, ranging from conventional to antibiotic-free and varying in sow breeding numbers (from 70 to 800), demonstrates the flexibility of the proposed approach, accommodating different farming systems. The study revealed three crucial considerations for future evaluations of tailor-made health plans. Firstly, placing compliance as the primary assessment indicator is a priority. Secondly, it is essential to tailor outcome indicators and monitoring periods according to each farm's specific health disorder. Lastly, a comprehensive understanding of the health disorder's evolution can be achieved through the amalgamation of multiple indicators. While the study does have limitations, such as the relatively short time window for assessment, the methodological framework and results are promising. Further, the discussion of the results raises several areas worthy of future investigation to improve compliance and address farmers' hesitations towards action (i.e., lack of willingness). More research in this context will be beneficial for veterinarians and practitioners, enhancing their understanding and positively impacting both farmers and animals. In conclusion, the study underscores the significant impact of tailor-made health plans on promoting positive changes in farm management. Assessing the effectiveness of these plans enables the refinement of new strategies and enhances the overall quality of work in animal production. The study by Levallois et al (1) sheds valuable light on the challenges and potentials of such plans, providing essential insights for pig farming practices. While further research and improvements are necessary, the study strongly emphasizes the pivotal role of individualized approaches in attaining improved farm management and enhancing animal welfare. 1. Levallois P, Leblanc-Maridor M, Scollo A, Ferrari P, Belloc C, Fourichon C. (2023). Combining several indicators to assess the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans in pig farms. Zenodo, 7789634. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7789634 2. Collineau L, Rojo-Gimeno C, Léger A, Backhans A, Loesken S, Nielsen EO, Postma M, Emanuelson U, grosse Beilage E, Sjölund M, Wauters E, Stärk KDC, Dewulf J, Belloc C, Krebs S. (2017). Herd-specific interventions to reduce antimicrobial usage in pig production without jeopardising technical and economic performance. Preventive veterinary medicine, 144:167-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2017.05.023 | Combining several indicators to assess the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans in pig farms | Levallois Pierre, Leblanc-Maridor Mily, Scollo Annalisa, Ferrari Paolo, Belloc Catherine, Fourichon Christine | <p style="text-align: justify;">A tailor-made health plan is a set of recommendations for a farmer to achieve and maintain a high health and welfare status. Tailored to each farm, it is intended to be an effective way of triggering change. This st... |  | Animal health, Veterinary science | Matteo Chincarini | 2023-03-31 19:02:35 | View | |
07 Feb 2022

Resilience: reference measures based on longer-term consequences are needed to unlock the potential of precision livestock farming technologies for quantifying this traitFriggens, N. C., Adriaens, I., Boré, R., Cozzi, G., Jurquet, J., Kamphuis, C., Leiber, F., Lora, I., Sakowski, T., Statham, J. and De Haas, Y. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5215797Measuring resilience in farm animals: theoretical considerations and application to dairy cowsRecommended by Aurélien Madouasse based on reviews by Ian Colditz and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Ian Colditz and 2 anonymous reviewers
Farm animals differ in their ability to respond to the many environmental challenges they face. Such challenges include infectious diseases, metabolic diseases resulting from inadequate coverage of dietary needs, as well as the diverse consequences of climate change. Various concepts exist to characterise the responses of animals to different types of challenges. This article by Friggens et al. (2022) focuses on resilience, providing a conceptual definition and proposing a method to quantify resilience in dairy cows. The first part of the paper provides a definition of resilience and highlights its differences and relations with the related concepts of robustness, and, to a lesser extent, resistance and tolerance. In essence, resilience is the ability of an animal to bounce back quickly after a challenge of limited duration. On the other hand, robustness is the ability of an animal to cope with conditions that are overall unfavourable. From these conceptual and intuitive definitions, there are several difficulties precluding the design of concrete methods to measure resilience. First, there is some degree of overlap between the concepts of resilience, robustness, resistance and tolerance. Secondly, resilience is a multidimensional concept whereby resilience to a given perturbation does not imply resilience to other types of perturbation, e.g. resilience to a challenge by a specific pathogen does not imply resilience to a nutritional challenge. A further difficulty in the measure of resilience is the fact that different animals may be exposed to challenges that are different in nature and in number. The authors argue that although resilience cannot be measured directly (it should be seen as a latent construct), it is possible to quantify it indirectly through its consequences. In the second part of the paper, the authors propose a method to quantify resilience of individual dairy cows. The method is based on the premise that resilient animals should be kept longer in their herd than non-resilient animals. The main criterion in the evaluation is therefore the ability of cows to re-calve. Each cow that is calving receives a certain number of points, to which, in each lactation, bonus points are added for higher milk production and penalty points are removed for each insemination after the first one, for each disease event and for each day of calving interval above some herd specific value. Therefore, cows have a resilience score in each lactation. They also have a lifetime resilience score obtained by summing the scores for all the lactations, that gets bigger as the cow has more calves, and that also takes the age at first calving into account. In a previous study, Adriaens et al. (2020) showed that higher resilience scores were associated with fewer drops in milk yield and more stable activity dynamics. Starting from theoretical considerations on the notion of resilience, this paper describes a concrete method to quantify animal-level resilience on farm. Such quantification will be useful for breeding and culling decisions. Finally, the general framework to design resilience measures that is presented will be useful to researchers working on the quantification of farm animal resilience using new methods and data sources.
References Adriaens I, Friggens NC, Ouweltjes W, Scott H, Aernouts B and Statham J 2020. Productive life span and resilience rank can be predicted from on-farm first-parity sensor time series but not using a common equation, across farms. Journal of Dairy Science 103, 7155-7171.https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2019-17826 Friggens, N.C. , Adriaens, I., Boré, R., Cozzi, G., Jurquet, J., Kamphuis, C., Leiber, F., Lora, I., Sakowski, T., Statham, J., De Haas, Y. (2022). Resilience: reference measures based on longer-term consequences are needed to unlock the potential of precision livestock farming technologies for quantifying this trait. Zenodo, 5215797, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Animal Science. https://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5215797 | Resilience: reference measures based on longer-term consequences are needed to unlock the potential of precision livestock farming technologies for quantifying this trait | Friggens, N. C., Adriaens, I., Boré, R., Cozzi, G., Jurquet, J., Kamphuis, C., Leiber, F., Lora, I., Sakowski, T., Statham, J. and De Haas, Y. | <p style="text-align: justify;">Climate change, with its increasing frequency of environmental disturbances puts pressures on the livestock sector. To deal with these pressures, more complex traits such as resilience must be considered in our mana... |  | Precision livestock farming | Aurélien Madouasse | 2021-08-20 15:34:13 | View | |
02 Sep 2021
A modelling framework for the prediction of the herd-level probability of infection from longitudinal dataAurélien Madouasse, Mathilde Mercat, Annika van Roon, David Graham, Maria Guelbenzu, Inge Santman Berends, Gerdien van Schaik, Mirjam Nielen, Jenny Frössling, Estelle Ågren, Roger Humphry, Jude Eze, George Gunn, Madeleine Henry, Jörn Gethmann, Simon J. More, Nils Toft, Christine Fourichon https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.10.197426Modelling freedom from disease - how do we compare between countries?Recommended by Rowland Raymond Kao based on reviews by Arata Hidano and 1 anonymous reviewerIn this paper, Madouasse et al. (2021) present a generalisable Bayesian method for calculating the probability that a herd is free from disease, based on its prior disease status, and using data (herd status over time over a sufficient number of herds to inform the model) and reasonable prior estimates of the sensitivity and specificity of tests being used to determine animal infection status. Where available, the modelling approach can also include relevant additional risk factors. By bringing all these factors together, it allows for most countries to use the same analytical approach on their data, with differences across datasets expressed in terms of the uncertainty around the central estimates. Having a single methodology that generates both a central estimate of disease freedom, and uncertainty thus provides the opportunity (given typically available data) to compare the probability of freedom across different systems. This is relevant in terms of the context of trade (since international trade of livestock in many cases depends on disease freedom). It is also important when evaluating, for example, transnational burdens of disease - and with different regulations in place in different countries, this is invaluable and can be used, for example, to assess risks of zoonotic infection including for zoonotic infection emergence. In the BVD example provided, the point is made that, since regular testing would probably pick up infection rapidly, the addition of risk factors is most valuable where testing is infrequent. This emphasizes the advantages of direct incorporation of risk factors into a single modelling framework. From a technical point of view, the analysis compares two different packages for the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) implementation necesary to run the model. They show that, while there are some slight systematic differences, the estimates provided by the two methods are similar to each other; as one method is approximate but substantially more stable and generally much more computationally efficient, this is an important outcome. Both implementations are freely available and with relevant additional software made similarly available by the authors. This is extremely welcome and should encourage its general adoption across different countries. No single model can of course account for everything. In particular, the reliance on past data means that there is an implicit assumption common to all purely statistical methods that the underlying risks have not changed. Thus projections to altered circumstances (changing underlying risk factors or systematic changes in testing or test performance) cannot so easily be incorporated, since these factors are complicated by the dynamics of infection that lie outside the modelling approach. Of course the well known quote from George Box that "all models are wrong" applies here - the generality of approach, statistical robustness and open source philosophy adopted make this model very useful indeed. Madouasse A, Mercat M, van Roon A, Graham D, Guelbenzu M, Santman Berends I, van Schaik G, Nielen M, Frössling J, Ågren E, Humphry RW, Eze J, Gunn GJ, Henry MK, Gethmann J, More SJ, Toft N, Fourichon C (2021) A modelling framework for the prediction of the herd-level probability of infection from longitudinal data. bioRxiv, 2020.07.10.197426, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.10.197426
| A modelling framework for the prediction of the herd-level probability of infection from longitudinal data | Aurélien Madouasse, Mathilde Mercat, Annika van Roon, David Graham, Maria Guelbenzu, Inge Santman Berends, Gerdien van Schaik, Mirjam Nielen, Jenny Frössling, Estelle Ågren, Roger Humphry, Jude Eze, George Gunn, Madeleine Henry, Jörn Gethmann, Sim... | <p>The collective control programmes (CPs) that exist for many infectious diseases of farm animals rely on the application of diagnostic testing at regular time intervals for the identification of infected animals or herds. The diversity of these ... |  | TEST, Veterinary epidemiology | Rowland Raymond Kao | 2020-07-23 08:13:18 | View | |
09 Feb 2024
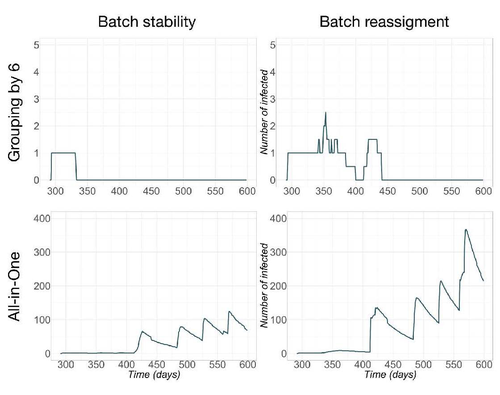
Pig herd management and infection transmission dynamics: a challenge for modellers.Vianney Sicard, Sébastien Picault, Mathieu Andraud https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.17.541128Towards models of infection transmission dynamicsRecommended by Marie-Pierre Letourneau Montminy based on reviews by Gustavo Machado and 1 anonymous reviewerEpidemics such as PRRSv-like virus in pig farms has tremendous impact on the competitiveness of swine production. However, its control requires an understanding of the complex interaction between pathogen transmission, disease impact, population dynamics and management. By using mechanistic epidemiological modelling, Sicard et al. (2023) open up a very interesting field of possibilities. This article describes work aimed at assessing the consequences of infections, taking into account the interaction between clinical outcomes and population dynamics. This study shows how this interaction can influence transmission dynamics at the herd level. It highlights the need to further explore this direction, integrating both disease impacts in breeding practices and structural changes in population dynamics, such as pig crossbreeding and grouping methodologies. Reference Sicard V, Picault S, Andraud M (2023) Pig herd management and infection transmission dynamics: a challenge for modellers. bioRxiv, 2023.05.17.541128. ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.17.541128
| Pig herd management and infection transmission dynamics: a challenge for modellers. | Vianney Sicard, Sébastien Picault, Mathieu Andraud | <p>The control of epidemics requires a thorough understanding of the complex interactions between pathogen transmission, disease impact, and population dynamics and management. Mechanistic epidemiological modelling is an effective way to address t... |  | Animal epidemiology modelling, Animal health, Bioinformatics, Farming systems, Infectious diseases, Mathematical modelling, Open science, Population dynamics, Veterinary epidemiology | Marie-Pierre Letourneau Montminy | 2023-05-22 15:07:37 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Karol B Barragán-Fonseca
Mohammed Gagaoua
Rachel Gervais
Florence Gondret
Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo
Anna Olsson
Seyed Abbas Rafat
Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas









