VEISSIER Isabelle
- UMR Herbivores, INRAE, Saine-Genes-Champanelle, France
- Animal behaviour , Animal cognition, Animal welfare, Precision livestock farming
- recommender
Recommendations: 2
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 2

Goats who stare at video screens – assessing behavioural responses of goats towards images of familiar and unfamiliar con- and heterospecifics
Gazing behaviour as a tool to study goat cognition
Recommended by Isabelle Veissier based on reviews by Richard Bon and 1 anonymous reviewerMany cognitive studies use paradigms based on active decision-making, that require that animals are motivated to participate and interested in the reward (e.g. Rivas-Blanco et al., 2023). By contrast, looking time paradigms, in which the visual attention of an animal to a stimulus is measured, requires little training and little action from the subject, and can be used without reinforcement (e.g. Wilson et al., 2023).
In this methodological paper, Jana Deutsch and her collaborators investigated the possibility of using a looking time paradigm to study perception and cognition in goats. The advantage of such a paradigm would be that it requires little training and can be used with no reinforcement. Goats were observed in front of two video screens presenting pictures of goats (familiar or not), of humans (familiar or not), or remaining white. The authors hypothesised that goats would pay more attention to pictures than to a white screen, would pay more attention to goats than to humans, and would discriminate familiar vs. unfamiliar beings. The goats had received previous positive contacts with the familiar humans. The goats were extensively habituated to the experimental set-up so that stress did not interfere in responses to testing. The stimuli were presented on the screens in a pseudorandomized and counterbalanced order.
As hypothesised, goats looked longer at screen with pictures, and longer when the picture was that of another goat (familiar or not) than of a human being. Goats however did not seem to discriminate between familiar and unfamiliar being, or were equally motivated by the two types of beings. Ear postures were also recorded but did not show a relation with looking time and were not related to the type of picture shown on screens. Therefore, the authors argue that looking time but not ear posture is considered appropriate to test discrimination abilities or preferences in goats. More studies are needed to check if goats can differentiate familiar vs. unfamiliar beings.
The experimental design is sound. The statistical analyses are rigorous and very relevant. The paper is clearly written.
I recommend the manuscript for publication for its originality and its quality; In addition, the paper bring findings – that looking time is an adequate paradigm in goats to analyse how they pay attention to stimuli – that have potential impacts on further studies in animal cognition.
References
Deutsch, J., Lebing, S., Eggert, A., Nawroth, C. (2024). Goats who stare at video screens – assessing behavioural responses of goats towards images of familiar and unfamiliar con- and heterospecifics. OSF, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/d4nzk
Rivas-Blanco, D., Monteiro, T., Virányi, Z., Range, F. (2024). Going back to “basics”: Harlow’s learning set task with wolves and dogs. Learning & Behavior. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13420-024-00631-6
Wilson, V. A. D., Bethell, E. J., Nawroth, C. (2023). The use of gaze to study cognition: limitations, solutions, and applications to animal welfare. Frontiers in Psychology, 14:1147278. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1147278
The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationship
Qualitative aspects of grunts vary with pigs' mental states
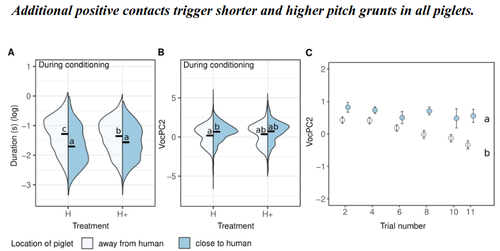
Recommended by Isabelle Veissier based on reviews by Matteo Chincarini and 1 anonymous reviewerVillain et al., (2023) investigated the structure of vocalisations in piglets in relation to human-animal-relationship. They first established a positive relationship by habituating piglets to be positively handled at weaning or later on after weaning. They then compared the reactions of piglets previously positively handled at weaning to that of non-handled piglets during tests in presence of a human (interacting or not), and also before and after the conditioning period when all piglets received positive contacts. They showed that the duration and frequency of grunts emitted in the presence of the human depends on previous contacts. More specifically, grunts are shorter and higher pitched in pigs that have been positively handled, in line with a positive human-animal relationship which is also observed through proximity of the piglets with the human. The authors concluded that the structure of pig vocalisation can reflect the quality of their relationship with humans.
The authors also showed that not only the response to humans is modified by positive contacts but also the general mood of piglets, with piglets positively handled at weaning emitting shorter grunts than non-handled piglets, whatever the context.
Another interesting finding is the temporality of behaviour of pigs habituated to positive contacts: during the first tests, they stay close to the human, probably being reassured by the proximity of the human. Then, when tests are repeated, they explore more the test room, using the human as an exploratory basis as already reported in the literature.
The hypotheses of the study are clear. The methods are reported in details so that the work is reproducible. The interpretation of results is sound. The manuscript is clearly written.
This paper brings new and original knowledge in the field of animals’ emotional responses and human-animal relationship: on the structure of grunts in relation to positive affects (positive emotion, positive mood) and on the temporality of the responses to human presence.
I recommend this manuscript for its originality and quality.
Isabelle Veissier
Villain, A.S., Guérin, C., Tallet, C., 2023. The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationship. bioRxiv 2022.03.15.484457, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.15.484457