
JAVANMARD Arash
Recommendations: 0
Review: 1
Review: 1
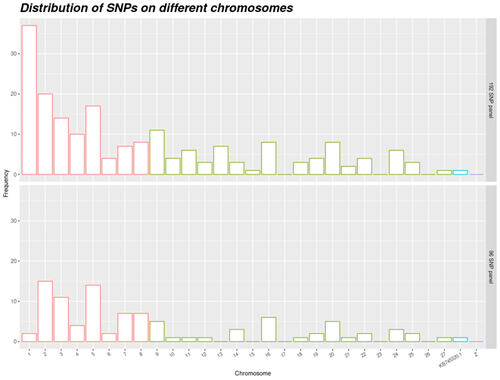
Cost-efficient assignment panel for ducks. Setup of a cost-efficient assignment panel for duck populations.
Providing innovative genetic solutions to the future challenges of the poultry industry: extraction of a small-sized Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) panel using factorial design for parentage assignment in a population consisting of pure and hybrid ducks
Recommended by Seyed Abbas Rafat based on reviews by Arash Javanmard and 2 anonymous reviewersOne of the achievements of animal genetics is that it finds solutions along with the emergence of new needs of the animal husbandry community or the adoption of new laws. Muir and Cheng (2013) research serves as a classic example of using the innovations of animal genetics to meet new legal challenges, such as the restriction of beak cutting in laying hens. Muir and Cheng (2013) investigated the genetic diversity to deal with the cannibalism of intact chickens. In 2021, the European Citizens' Initiative urged the European Commission to legislate against the use of cages for farm animals in the livestock industry. Chapuis et al., (2024) presented a successful solution to the poultry industry about this (future) law by presenting a cost-efficient assignment SNP panel.
In animal breeding, access to pedigree information is necessary for genetic progress. Since the 1970s, the development of genomic science and molecular techniques has shown their ability in this field. Despite the substantial reduction of genotyping costs in the last 20 years, the practical use of genome-wide genotyping for thousands of SNPs remains challenging. Therefore, the search for a small, cost-effective SNP panel is ongoing, with objectives including genetic diversity (Viale et al., 2017), product traceability (Dominik et al., 2021), species and hybrid identification (Harmoinen et al., 2021) and pedigree construction in wild populations (Ekblom et al., 2021). Furthermore, especially in recent decades, small panels of markers have been proposed for parentage assignment in different animals. For example, Domínguez-Viveros et al., (2020) developed panels with 42 to 63 markers for different sheep breeds in Mexico. Similar panels for parentage assignment have been proposed for salmon (May et al., 2020), rainbow trout (Liu et al., 2016), French sheep (Tortereau et al., 2017), Spanish sheep (Calvo et al., 2021), and European bison (Wehrenberg et al., 2024), with marker numbers of 142, 95, 180, 173, and 96, respectively. Massault et al., (2021) showed by simulation that a panel with at least 50 markers is sufficient for progeny assignment in pearl oysters. These examples highlight that extracting a small panel of markers (usually less than 200) from the total genotyping introduced in different species, can open new horizons for applying genomic information in animal breeding.
Chapuis et al. (2024) addressed the challenge of finding an efficient set of markers that can be used in the hybridization of two species of the Pekin duck and the Muscovy duck. They used KASPar technology to setup a panel, with SNPs existing in both species and their hybrids. This panel has sufficient polymorphism to use in practice. Thus, it can be considered as a step forward compared to previous work done on microsatellites. A final list of SNPs was constructed from a reference set comprising 600 K genotyping of Anas platyrhynchos, Cairina moschata and mule duck.
In addition to developing of a cost-efficient assignment panel, the work of Chapuis et al. (2024) presented a factorial design to maintain genetic diversity while considering specificities of duck production. The use of factorial design in avian pedigreed populations is relatively novel, making this research particularly innovative. The study's approach to factorial design in populations with limited size may be generalized to similar poultry species. Furthermore, sufficient effective size of population is selected. So, the panel can be used in other populations outside the tested populations. A notable feature of this panel is the use of neutral SNPs, which ensures that markers will not be lost due to future selection pressures over time.
The paper of Chapuis et al. (2024) exemplifies the application of molecular genetics to address challenges in the poultry industry. The use of kinship matrix instead of relationship matrix, taking into account the unique characteristics of duck production, could be another novelty of the paper. According to the reviewers' comments, the results can be beneficial in the future, particularly with the introduction of the specific factorial design.
References
Calvo JH, Serrano M, Tortereau F, Sarto P, Iguacel LP, Jiménez MA, Folch J, Alabart JL, Fabre S and Lahoz B (2021). Development of a SNP parentage assignment panel in some North-Eastern Spanish meat sheep breeds. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research 18, e0406. https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2020184-16805
Chapuis H, Brard-Fudulea S, Hazard A, Vignal A, Demars J, Rouger R, Teissier M, Gilbert H (2024). Cost-efficient assignment panel for ducks. Setup of a cost-efficient assignment panel for duck populations.: An illustration with experimental data. HAL, hal-04542880, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04542880
Domínguez-Viveros J, Rodríguez-Almeida FA, Jahuey-Martínez FJ, Martínez-Quintana JA, Aguilar-Palma GN, Ordoñez-Baquera P (2020). Definition of a SNP panel for paternity testing in ten sheep populations in Mexico, Small Ruminant Research ,193,106262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2020.106262
Dominik S, Duff CJ, Byrne AI, Daetwyler H, Reverter A (2021). Ultra-small SNP panels to uniquely identify individuals in thousands of samples. Animal Production Science 61, 1796–1800. https://doi.org/10.1071/AN21123
Ekblom R, Aronsson M, Elsner-Gearing F, Johansson M, Fountain T, Persson J (2021). Sample identification and pedigree reconstruction in Wolverine (Gulo gulo) using SNP genotyping of non-invasive samples. Conservation Genetics Resources 13, 261–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-021-01208-5
Harmoinen J, von Thaden A, Aspi J, Kvist L, Cocchiararo B, Jarausch A, Gazzola A, Sin T, Lohi H, Hytönen MK, Kojola I, Stronen AV, Caniglia R, Mattucci F, Galaverni M, Godinho R, Ruiz-González A, Randi E, Muñoz-Fuentes V, Nowak C (2021). Reliable wolf-dog hybrid detection in Europe using a reduced SNP panel developed for non-invasively collected samples. BMC Genomics 22, 473. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07761-5
Liu S, Palti Y, Gao G, Rexroad CE (2016). Development and validation of a SNP panel for parentage assignment in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 452, 178–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.11.001
Massault C, Jones DB, Zenger KR, Strugnell JM, Barnard R, Jerry DR (2021). A SNP parentage assignment panel for the silver lipped pearl oyster (Pinctada maxima). Aquaculture Reports 20, 100687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100687
May SA, McKinney GJ, Hilborn R, Hauser L, Naish KA (2020). Power of a dual-use SNP panel for pedigree reconstruction and population assignment. Ecology and Evolution 10, 9522–9531. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.6645
Muir WM, Cheng HW(2013). Genetics and the Behaviour of Chickens: Welfare and Productivity. In Genetics and the Behaviour of Domestic Animals. Vol. 2 (2nd ed.). pp. 1–30.ISBN: 9780128100165
Tortereau F, Moreno CR, Tosser-Klopp G, Servin B, Raoul J (2017). Development of a SNP panel dedicated to parentage assignment in French sheep populations. BMC Genetics 18, 50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-017-0518-2
Viale E, Zanetti E, Özdemir D, Broccanello C, Dalmasso A, De Marchi M, Cassandro M (2017). Development and validation of a novel SNP panel for the genetic characterization of Italian chicken breeds by next-generation sequencing discovery and array genotyping. Poultry Science 96, 3858–3866. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pex238
Wehrenberg G, Tokarska M, Cocchiararo B, Nowak C (2024). A reduced SNP panel optimised for non-invasive genetic assessment of a genetically impoverished conservation icon, the European bison. Scientific Reports 14, 1875. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-51495-9