
SPENCER Jennifer
Recommendations: 0
Review: 1
Review: 1
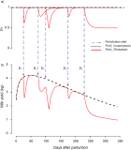
Lactation curve model with explicit representation of perturbations as a phenotyping tool for dairy livestock precision farming.
Developing smart fitting algorithms to identify random perturbations in time-series data
Recommended by Luis Tedeschi based on reviews by Alberto Atzori, Jennifer Spencer and 1 anonymous reviewerThe ability to adequately characterize the lactation curve of livestock is important not only to ensure proper nutrition of the lactating animal but, among many other benefits, it can assist in diagnosing the incidence of diseases, predicting the quantity of milk production, and comparing animals within the herd for managerial strategies such as culling. Eventually, such smart fitting algorithms can lead to improved genetic selection of more productive animals after genetic-unrelated noises are removed from the data, systematically.
The manuscript by Ben Abdelkrim et al. developed and explained an algorithm to detect perturbations in lactation curves of dairy goats. Researchers have been interested in accurately describing lactation curves since the early-1960s. Johansson [1] proposed a nonlinear decay function, Nelder [2] described an inverse polynomial, and Wood [3] proposed the incomplete gamma function to describe milk production of dairy cows. Unfortunately, many of the lactating animals that yielded lactation curves that did not comply with the typical, expected pattern of milk production were usually discarded and, until then, efforts to address this lack of adherence were not conducted. The recommended manuscript provides a different perspective in which rather than discarding the lactation profile, one can model the perturbations of the lactation curve as an attempt to identify possible problems (e.g., mastitis) and minimize their occurrence. Such an algorithm is important to separate females that show resilient attributes from those females that show sustainable attributes, as per existing definitions proposed by Tedeschi et al. [4].
The recommended manuscript proposes the Perturbed Lactation Model to explicitly account for multiple perturbations in the time-series milk production in dairy goats. When perturbations occur in biological processes, a typical negative impact is observed in the animal’s response, but on rare occasions, positive impacts can occur. In this case, the animal responds positively to the perturbation (i.e., responsive), and as a result, there is an increase in their output when compared to unperturbed animals. The recommended manuscript only considered negative impacts due to perturbations in the lactation curve of dairy goats. Future modifications should include positive responses due to perturbations. In this case, animals would be “positively responsive” to perturbations, and examples of such behavior include feed intake and growth curves.
References
[1] Johansson, I. (1961). Genetic Aspects of Dairy Cattle Breeding. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, IL.
[2] Nelder, J. A. (1966). Inverse polynomials, a useful group of multi-factor response functions. Biometrics. 22 (1):128-141. doi: 10.2307/2528220
[3] Wood, P. D. P. (1967). Algebraic model of the lactation curve in cattle. Nature. 216 (5111):164-165. doi: 10.1038/216164a0
[4] Tedeschi, L. O., J. P. Muir, D. G. Riley, and D. G. Fox. (2015). The role of ruminant animals in sustainable livestock intensification programs. Int. J. Sustainable Dev. World Ecol. 22 (5):452-465. doi: 10.1080/13504509.2015.1075441