Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender▲ | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
20 Dec 2021

Quantifying growth perturbations over the fattening period in swine via mathematical modellingManuel Revilla, Guillaume Lenoir, Loïc Flatres-Grall, Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo, Nicolas C Friggens https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.22.349985An innovative modelling approach to enhance the quality of the quantification of pig resilience during the entire fattening period: Towards an individual pig resilience indexRecommended by Mohammed Gagaoua based on reviews by Arata Hidano, Ludovic Brossard and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Arata Hidano, Ludovic Brossard and 2 anonymous reviewers
The identification of reliable estimates of growth potential and resilience over the fattening period in large populations is a challenge in actual swine breeding conditions. To overcome this drawback, the study by Revilla et al. 2021 in the frame of precision livestock farming aimed to propose an innovative modelling approach, in addition to previous studies from the same group (Revilla et al. 2019), to enhance the quality of the quantification of pig resilience during the entire fattening period. The authors developed a model that quantifies an “individual pig resilience indicator” based on longitudinal data, for instance body weight, recorded routinely by a commercially available automatic feeding system. Revilla and co-workers considered in their study two mainly commercialised pure pig breeds these being Piétrain including Piétrain Français NN Axiom line (Pie NN) free from halothane-sensitivity (ryanodine receptor gene, RYR1) and Piétrain Français Axiom line positive to this gene and Duroc. Therefore, the authors investigated the potential of improving resilience of swine livestock through inclusion for the first time of an “individual pig resilience indicator” in breeding objectives. A database of 13 093 boars (approximately 11.1 million of weightings) belonging to Pie (n= 5 841), Pie NN (n = 5 032) and Duroc (n= 2 220) finished under ad libitum feeding, high sanitary level and controlled temperature was used to develop robust models. The authors checked the three datasets (for each pig breed) independently to explore the variation and gaps (a data pre-treatment procedure) to ensure high quality data for the modelling approach. Then, they applied the Gompertz model and linear interpolation on body weight data to quantify individual deviations from the expected production, allowing the creation of the ABC index. For the modelling, the authors applied a two-step mathematical model approach by first establishing a theoretical growth curve of each animal, while the second step aimed to build the actual perturbed growth curve. The heritability of the index ranged from 0.03 to 0.04, with similar heritability between Piétrain and Duroc breeds. Moreover, moderate genetic relationships were computed between the proposed index and important phenotypic traits in swine production likely BF100: backfat thickness at 100kg; LD100: longissimus dorsi thickness at 100kg; ADG: average daily gain during control and FCR: feed conversion ratio. Developing models able to capture perturbations during the fattening period is a challenge in swine breeding industry. The model and methodology proposed by the authors in this innovative work (although preliminary and with low heritabilities) would help overcome such limit and facilitate a real implementation at large scale in pig breeding system. The modelling approach further offers an opportunity to develop a selection criterion to improve resilience in swine breeding conditions. To explore the full potential of this modelling approach, a larger database and other factors such as breed, behaviour and feeding behaviour of the animals, rearing practices, management and environment conditions, age… etc. are worthy to consider. In the future, more in depth measurements of behaviour that can be computed for example using computer vision should be desirable to increase the robustness of the proposed model. References Revilla, M., Friggens, N.C., Broudiscou, L.P., Lemonnier, G., Blanc, F., Ravon, L., Mercat, M.J., Billon, Y., Rogel-Gaillard, C., Le Floch, N. and Estellé, J. (2019). Towards the quantitative characterisation of piglets’ robustness to weaning: a modelling approach. Animal, 13(11), 2536-2546. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731119000843 Revilla M, Lenoir G, Flatres-Grall L, Muñoz-Tamayo R, Friggens NC (2021). Quantifying growth perturbations over the fattening period in swine via mathematical modelling. bioRxiv, 2020.10.22.349985, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.22.349985 | Quantifying growth perturbations over the fattening period in swine via mathematical modelling | Manuel Revilla, Guillaume Lenoir, Loïc Flatres-Grall, Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo, Nicolas C Friggens | <p>Background: Resilience can be defined as the capacity of animals to cope with short-term perturbations in their environment and return rapidly to their pre-challenge status. In a perspective of precision livestock farming, it is key to create i... |  | Animal genetics, Animal health, Farming systems, Mathematical modelling, Precision livestock farming | Mohammed Gagaoua | 2020-10-26 11:47:08 | View | |
31 Jan 2020

OneARK: Strengthening the links between animal production science and animal ecologyDelphine Destoumieux-Garzón, Pascal Bonnet, Céline Teplitsky, François Criscuolo, Pierre-Yves Henry, David Mazurais, Patrick Prunet, Gilles Salvat, Philippe Usseglio-Polatera, Etienne Verrier and Nicolas Friggens https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3632731When scientific communities intertwineRecommended by Pauline Ezanno based on reviews by Rowland Raymond Kao, Arata Hidano and 1 anonymous reviewerScientific research can be seen by some as a competitive territory: competition of opinions, concepts, publications, competition for funding. Fortunately, it is above all a territory of sharing and cross-fertilization of ideas. It is gradually becoming a territory of productive interdisciplinary collaborations, despite persistent resistance to making borders more permeable [1]. At the crossroads of worlds, many challenges must be met for communities to understand each other, to be able to communicate with one another, and to benefit mutually from scientific interactions [2]. Delphine Destoumieux-Garzon and co-authors [3] propose to stimulate a single Animal Research Kinship (OneARK) to promote the crossing of the scientific communities in animal production and animal ecology. These two communities share many concepts and methods, which, while they are based on marked specificities (natural versus artificial systems), also and above all have common points that need to be explored more closely. Seven concepts of shared interest to improve the resilience and sustainability of animal population systems were explored by the authors: selection, system viability, system management, animal adaptability, inter-individual diversity in systems, agroecology, and animal monitoring. This foundation stone paves the way for a finer integration between these two communities, which are close and yet distant, and which are slowly getting to know, understand, and recognize each other. References [1] Ledford, H. (2015). How to solve the world’s biggest problems. Nature, 525, 308–311. doi: 10.1038/525308a | OneARK: Strengthening the links between animal production science and animal ecology | Delphine Destoumieux-Garzón, Pascal Bonnet, Céline Teplitsky, François Criscuolo, Pierre-Yves Henry, David Mazurais, Patrick Prunet, Gilles Salvat, Philippe Usseglio-Polatera, Etienne Verrier and Nicolas Friggens | <p>1. Wild and farmed animals are key elements of natural and managed ecosystems that deliver functions such as pollination, pest control and nutrient cycling within the broader roles they play in contributing to biodiversity and to every category... |  | Agricultural sustainability, Animal genetics, Animal welfare, Ecology, Precision livestock farming, Veterinary epidemiology | Pauline Ezanno | 2019-07-05 15:33:21 | View | |
02 Sep 2021
A modelling framework for the prediction of the herd-level probability of infection from longitudinal dataAurélien Madouasse, Mathilde Mercat, Annika van Roon, David Graham, Maria Guelbenzu, Inge Santman Berends, Gerdien van Schaik, Mirjam Nielen, Jenny Frössling, Estelle Ågren, Roger Humphry, Jude Eze, George Gunn, Madeleine Henry, Jörn Gethmann, Simon J. More, Nils Toft, Christine Fourichon https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.10.197426Modelling freedom from disease - how do we compare between countries?Recommended by Rowland Raymond Kao based on reviews by Arata Hidano and 1 anonymous reviewerIn this paper, Madouasse et al. (2021) present a generalisable Bayesian method for calculating the probability that a herd is free from disease, based on its prior disease status, and using data (herd status over time over a sufficient number of herds to inform the model) and reasonable prior estimates of the sensitivity and specificity of tests being used to determine animal infection status. Where available, the modelling approach can also include relevant additional risk factors. By bringing all these factors together, it allows for most countries to use the same analytical approach on their data, with differences across datasets expressed in terms of the uncertainty around the central estimates. Having a single methodology that generates both a central estimate of disease freedom, and uncertainty thus provides the opportunity (given typically available data) to compare the probability of freedom across different systems. This is relevant in terms of the context of trade (since international trade of livestock in many cases depends on disease freedom). It is also important when evaluating, for example, transnational burdens of disease - and with different regulations in place in different countries, this is invaluable and can be used, for example, to assess risks of zoonotic infection including for zoonotic infection emergence. In the BVD example provided, the point is made that, since regular testing would probably pick up infection rapidly, the addition of risk factors is most valuable where testing is infrequent. This emphasizes the advantages of direct incorporation of risk factors into a single modelling framework. From a technical point of view, the analysis compares two different packages for the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) implementation necesary to run the model. They show that, while there are some slight systematic differences, the estimates provided by the two methods are similar to each other; as one method is approximate but substantially more stable and generally much more computationally efficient, this is an important outcome. Both implementations are freely available and with relevant additional software made similarly available by the authors. This is extremely welcome and should encourage its general adoption across different countries. No single model can of course account for everything. In particular, the reliance on past data means that there is an implicit assumption common to all purely statistical methods that the underlying risks have not changed. Thus projections to altered circumstances (changing underlying risk factors or systematic changes in testing or test performance) cannot so easily be incorporated, since these factors are complicated by the dynamics of infection that lie outside the modelling approach. Of course the well known quote from George Box that "all models are wrong" applies here - the generality of approach, statistical robustness and open source philosophy adopted make this model very useful indeed. Madouasse A, Mercat M, van Roon A, Graham D, Guelbenzu M, Santman Berends I, van Schaik G, Nielen M, Frössling J, Ågren E, Humphry RW, Eze J, Gunn GJ, Henry MK, Gethmann J, More SJ, Toft N, Fourichon C (2021) A modelling framework for the prediction of the herd-level probability of infection from longitudinal data. bioRxiv, 2020.07.10.197426, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.10.197426
| A modelling framework for the prediction of the herd-level probability of infection from longitudinal data | Aurélien Madouasse, Mathilde Mercat, Annika van Roon, David Graham, Maria Guelbenzu, Inge Santman Berends, Gerdien van Schaik, Mirjam Nielen, Jenny Frössling, Estelle Ågren, Roger Humphry, Jude Eze, George Gunn, Madeleine Henry, Jörn Gethmann, Sim... | <p>The collective control programmes (CPs) that exist for many infectious diseases of farm animals rely on the application of diagnostic testing at regular time intervals for the identification of infected animals or herds. The diversity of these ... |  | TEST, Veterinary epidemiology | Rowland Raymond Kao | 2020-07-23 08:13:18 | View | |
11 Dec 2023
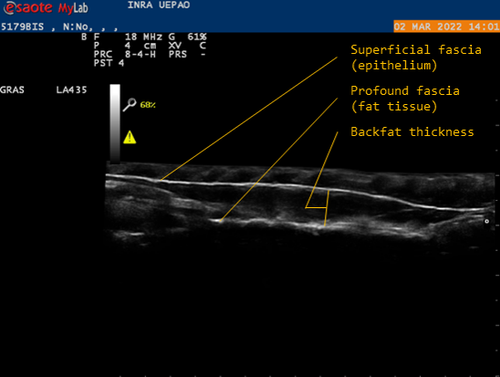
Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotypingNicolas Bédère, Joëlle Dupont, Yannick Baumard, Christophe Staub, David Gourichon, Frédéric Elleboudt, Pascale Le Roy, Tatiana Zerjal https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04172576Towards a better optimization of the genetic improvement of chicken breeds: Introduction of simple phenotypic traits related to body composition for easy measurement in the selection programs of laying hens.Recommended by Seyed Abbas Rafat based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In genetic selection, simplistic model of single-trait selection is usually considered, and the response to such approach is estimated using simple models. In practice, however, plant and animal breeders always deal with the selection of several traits, hence making the selection process very complex. Therefore, the simultaneous genetic improvement of several traits has always been one of the goals of livestock, including poultry breeding (Falconer, 1972). Studies that examine the indirect effects of selection on economic traits are eagerly awaited. In this context, the results of the study by Bédère et al., (2023) gives new insights about phenotypic and genotypic relationships between body reserves traits in laying hens. The authors aimed to propose novel data about the genetic architecture of traits related to body fat by measuring a series of phenotypic traits with relatively an easy approach. The authors further aimed to test and validate the phenotyping of backfat thickness as an indicator of the overall fatness of laying hens. Thus, the study allowed providing new evidence regarding the genetic determination of the backfat trait in chicken breeds. The authors first estimated the effect of selection on the residual feed intake (trait x) on the trait of body reserves (trait y). In fact, divergent selection experiments are a fundamental research tool that allow revealing significant amount of data related to the possible span of genetic improvement for traits of interest. Consequently, by analyzing data from a divergent selection experiment, associations have been estimated between a number of feed-dependent traits that have practical use for chicken breeders. Estimation of the correlations between traits is under question in terms of the theory of genetics and their application in multi-trait selection. As a major finding of the study, the observation of a bimodal distribution of backfat in both lines and the heterogeneity of the variances between families allowed suggesting a possible major gene, which could be investigated in future studies using for instance quantitative genetics. Body composition is continually studied in broilers chicken, but this aspect of chicken genetic is more detailed in laying hens. The current findings are worthy to validate using several approaches. In fact, one of the limitations of the study can be related to other statistical models that can be built. For example, the study revealed high correlations between egg production and body weight, thus body weight could be considered as a covariate in regression models. Moreover, the principal trait of selection (based on the residual feed intake) could be considered. References: Falconer, D. S. (1972). Introduction to Quantitative Genetics. Publisher: Ronald Press Company. pp 365. Bédère, N., Dupont, J., Baumard, Y., Staub, C., Gourichon, D., Elleboudt, F., Le Roy, P., Zerjal, T. (2023). Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotyping. HAL ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04172576 | Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotyping | Nicolas Bédère, Joëlle Dupont, Yannick Baumard, Christophe Staub, David Gourichon, Frédéric Elleboudt, Pascale Le Roy, Tatiana Zerjal | <p>In this study, we pursued three primary objectives: firstly to test and validate the phenotyping of backfat thickness as an indicator of the overall fatness of laying hens; secondly, to estimate genetic parameters for this trait; thirdly, to st... |  | Animal genetics, Poultry, Statistical genetics | Seyed Abbas Rafat | 2023-07-27 17:09:10 | View | |
29 Jan 2024
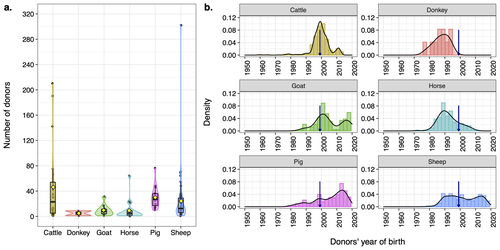
Assessing the potential of germplasm collections for the management of genetic diversity: the case of the French National CryobankAlicia Jacques, Delphine Duclos, Coralie Danchin-Burge, Marie-Jose Mercat, Michele Tixier-Boichard, Gwendal Restoux https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.19.549644Exploring Genetic Diversity Management: Unveiling the Potential of Germplasm Collections in the French National CryobankRecommended by Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas based on reviews by Roy Costilla and 1 anonymous reviewerThe study by Jacques et al. (2024) addresses a critical concern in the context of genetic diversity erosion in domesticated animal populations. The research uses data from the cryopreserved resources from the French National Cryobank to manage genetic diversity in livestock species. The authors employ a comprehensive methodology to propose novel biodiversity metrics to characterize the status of genetic diversity of cryopreserved collections including cattle, sheep, goat, horse, donkey, and pig livestock species. The findings reveal significant variations of genetic diversity at species and breed levels. Breeds with a large commercial distribution had more donors in the collection than local breeds. The authors propose a practical framework for assessing germplasm collections, providing a valuable tool for planning and managing collections at both national and international levels. The study also highlights the usefulness of the Gini-Simpson and effective donor numbers indices to plan a more efficient sampling, whereas the index of diversity impact can be employed in the selection of the most suitable donors for immediate use, based on pedigree but also using genetic markers. In resume, this study makes a significant contribution to the field by offering a framework for the assessment of germplasm collections. Its innovative metrics provide insights that could guide strategic decision-making in planning, managing, and utilizing cryopreserved resources. This research is relevant and can benefit conservationists, and population genetics working towards the preservation and sustainable use of genetic resources in livestock species. Reference Jacques, A., Duclos, D., Danchin-Burge, C., Mercat, M. J., Tixier-Boichard M., Restoux, G. (2024). Assessing the potential of germplasm collections for the management of genetic diversity: the case of the French National Cryobank. bioRxiv 2023.07.19.549644. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.19.549644
| Assessing the potential of germplasm collections for the management of genetic diversity: the case of the French National Cryobank | Alicia Jacques, Delphine Duclos, Coralie Danchin-Burge, Marie-Jose Mercat, Michele Tixier-Boichard, Gwendal Restoux | <p>Through a combination of selective pressure and genetic drift, there has been a notable erosion of genetic diversity in domesticated animal populations. In response, many countries, including France, have developed gene banks in order to conser... |  | Animal genetics | Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas | 2023-07-20 19:08:40 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Karol B Barragán-Fonseca
Mohammed Gagaoua
Rachel Gervais
Florence Gondret
Francois Meurens
Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo
Anna Olsson
Seyed Abbas Rafat
Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas









