Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender▼ | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
05 Dec 2019
Effects of feeding treatment on growth rate and performance of primiparous Holstein dairy heifersYannick Le Cozler, Julien Jurquet, Nicolas Bedere https://doi.org/10.1101/760082Optimizing growth rate of dairy heifers through nutrition to maximize reproduction and productionRecommended by Luis Tedeschi based on reviews by Emilio Mauricio Ungerfeld and 2 anonymous reviewersThe idea of altering the growth rate of replacement heifers to improve reproductive and productive indicators of dairy cattle is not new. In the late 1970s, Gill and Allaire [1] indicated that the first parturition between 22.5 to 23.5 months of age yielded the optimum lifetime performance as long as the heifers had adequate body size [2]. Since 1980s, many studies have been conducted to understand the partitioning of energy between growth and lactation, including the impact of growth rates on the heifer puberty [3] as well as growth and development of the mammary gland [4,5]. The senior author of the recommended study has written previously about this research topic [6]. In the present manuscript, Le Cozler et al. studied the effect of feeding programs to increase the growth rate of late-born heifers to catch up with the growth of those born earlier in the calving season on their reproductive and productive performance. The authors analyzed 217 heifers for three consecutive years, split into three dietary treatments: control (C), accelerated growth rate from birth to 6 months of age (ID1), or accelerated growth rate from birth to 12 months of age (ID2). In this study, the late-born heifers receiving the ID2 treatment were able to partially reach the bodyweight of the early-born heifers at 24 months of age. In part, the incomplete understanding of the prioritization of the use of energy (and other nutrients) for different physiological stages (e.g., maintenance, growth, lactation, and pregnancy) of the dairy animal [7] undercuts the development of more robust feeding strategies to improve the reproductive and productive performance of the animal. In the recommended study by Le Cozler et al., although there was no impact on reproductive performance among groups, heifers in the group ID2 produced less milk (about 400 kg for the whole first lactation) than heifers in the groups C and ID1, apparently suggesting that energy allocation for growth had priority over that needed for lactation. The question then becomes what would have happened with energy partitioning if energy intake was restricted. Studies like this one are important to shed some light on the prioritization of the use of energy and other nutrients in support of growth, pregnancy, and lactation of dairy animals, and how compensatory growth differs between meat versus dairy growing animals, both physiologically and energetically. References [1] Gill, G. S., & Allaire, F. R. (1976). Relationship of Age at First Calving, Days Open, Days Dry, and Herdlife to a Profit function for Dairy Cattle1. Journal of Dairy Science, 59(6), 1131–1139. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(76)84333-0 | Effects of feeding treatment on growth rate and performance of primiparous Holstein dairy heifers | Yannick Le Cozler, Julien Jurquet, Nicolas Bedere | <p>The objective of this study was to investigate effects of feeding-rearing programs that aim for first calving at 20-27 months (mo) of age on growth, reproduction and production performance of Holstein cows at nulliparous and primiparous stages.... | Cattle production, Reproduction, Ruminant nutrition | Luis Tedeschi | 2019-09-09 09:22:36 | View | ||
16 Apr 2021
Modelling the impact of the macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis on rumen microbial fermentation and methane productionRafael Muñoz-Tamayo , Juana C. Chagas, Mohammad Ramin, Sophie J. Krizsan https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.09.374330Understanding the mechanisms behind natural bioactive compounds that can potentially reduce methane production in anaerobic conditions. A case study of Asparagopsis taxiformisRecommended by Luis Tedeschi based on reviews by Alberto Atzori, Henk van Lingen and 2 anonymous reviewersNaturally occurring compounds that can reduce methane production in anaerobic conditions have been studied for quite some time as feasible approaches to mitigate methane production in ruminant animals, especially those of commercial importance. Asparagopsis taxiformis (red algae) and Dictyota bartayresii (brown algae) are effective inhibitors of methane synthesis under in vitro anaerobic fermentation systems (Machado et al., 2014) likely because of their high concentration of secondary metabolites that are toxic to the typical rumen microbiota, including protozoa. In addition to phytoplankton (Palmer and Reason, 2009), Asparagopsis contains a high concentration of haloform compounds (e.g., bromoform, chloroform) while Dictyota has a high concentration of isoprenoid terpenes. Despite the economic and biological impact of diverse phytochemicals on reducing methane production in ruminant animals (Tedeschi et al., 2021), haloform compounds’ environmental impact and safety, in particular, are still unclear. In the present study, Munõz-Tamayo and collaborators (2021) listed relevant literature about the impact of A. taxiformis on ruminal methane production. Concurrent to the understanding of mechanisms and biology behind the reduction of ruminal methane, mathematical models can lead the way to enhance the effectiveness of feeding A. taxiformis under commercial applications. Thus, in the present study, Munõz-Tamayo and collaborators (2021) sought to develop a mathematical model to understand the rumen fermentation changes in vitro experimentation containing extract of A. taxiformis by adapting a previously documented model by Muñoz-Tamayo et al. (2016). Modeling development, calibration, and evaluation steps should be independent of each other, requiring complete, distinct, and separate databases (Tedeschi, 2006). However, in rare circumstances where such requirements cannot be met because data availability is scarce, the cross-validation technique, when possible, should be considered to assess data dispersion’s effects on model adequacy. In other situations, clear reasoning for failing to do so must be addressed in the paper. In the present paper, Munõz-Tamayo and collaborators (2021) explained the limitations in their modeling efforts were primarily due to the lack of ideal data: “experiments with simultaneous dynamic data of bromoform, volatile fatty acids, hydrogen, and methane.” Regardless of the availability of ideal data, improvements in the conceptual model are warranted to include amino acids and branched-chain fatty acids fermentation dynamics in the rumen and the fluctuations in ruminal pH. References Machado L, Magnusson M, Paul NA, Nys R de, Tomkins N (2014) Effects of Marine and Freshwater Macroalgae on In Vitro Total Gas and Methane Production. PLOS ONE, 9, e85289. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085289 Muñoz-Tamayo R, Chagas JC, Ramin M, Krizsan SJ (2021) Modelling the impact of the macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis on rumen microbial fermentation and methane production. bioRxiv, 2020.11.09.374330, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.09.374330 Muñoz-Tamayo R, Giger-Reverdin S, Sauvant D (2016) Mechanistic modelling of in vitro fermentation and methane production by rumen microbiota. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 220, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.07.005 Palmer CJ, Reason CJ (2009) Relationships of surface bromoform concentrations with mixed layer depth and salinity in the tropical oceans. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 23. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GB003338 Tedeschi LO (2006) Assessment of the adequacy of mathematical models. Agricultural Systems, 89, 225–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2005.11.004 Tedeschi LO, Muir JP, Naumann HD, Norris AB, Ramírez-Restrepo CA, Mertens-Talcott SU (2021) Nutritional Aspects of Ecologically Relevant Phytochemicals in Ruminant Production. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.628445 | Modelling the impact of the macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis on rumen microbial fermentation and methane production | Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo , Juana C. Chagas, Mohammad Ramin, Sophie J. Krizsan | <p>Background: The red macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis is a potent natural supplement for reducing methane production from cattle. A. taxiformis contains several anti-methanogenic compounds including bromoform that inhibits directly methanogene... |  | Agricultural sustainability, Animal nutrition modelling, Emissions , Mathematical modelling, Microbial fermentation, Rumen microbiology, Rumen microbiome | Luis Tedeschi | 2020-11-17 06:28:29 | View | |
14 Oct 2020

Determining insulin sensitivity from glucose tolerance tests in Iberian and Landrace pigsJ. M. Rodríguez-López, M. Lachica, L. González-Valero, I. Fernández-Fígares https://doi.org/10.1101/2019.12.20.884056Iberian pigs: more than excellent ham!Recommended by Jordi Estellé based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersIberian pigs represent a treasured resource that allows the maintenance of their “montanera” traditional breeding system and, thus, contributes to the socioeconomic sustainability of the rural areas in the south-western regions of Iberian Peninsula. While the excellence of Iberian meat products is widely recognized, the idea of using Iberian pigs as biomedical models is currently emerging. Interestingly, due to the particular fatty acid metabolism of this porcine breed, Iberian pigs have been proposed as models for type 2 diabetes (Torres-Rovira et al. 2012) or obesity-related renal disease (Rodríguez et a. 2020). In the present manuscript, Rodríguez-López et al. provide further insights on the particularities of “obese” Iberian pigs by comparing their insulin sensitivity in a glucose tolerance test with that of commercial “lean” Landrace pigs. The authors compared four Iberian pigs with five Landrace pigs in an intense time-series following an intra-arterial glucose tolerance test and measuring insulin, glucose, lactate, triglycerides, cholesterol, creatinine, albumin and urea plasma levels. Several of these parameters showed significant differences between both breeds, with some of them being compatible with an early stage of insulin resistance in Iberian pigs. These results are relevant from an animal production perspective, but provide also further evidence for considering the Iberian pigs as a suitable biomedical model for obesity-related disorders. References [1] Torres-Rovira, L., Astiz, S., Caro, A., Lopez-Bote, C., Ovilo, C., Pallares, P., Perez-Solana, M. L., Sanchez-Sanchez, R., & Gonzalez-Bulnes, A. (2012). Diet-induced swine model with obesity/leptin resistance for the study of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. The Scientific World Journal, 510149. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/510149 | Determining insulin sensitivity from glucose tolerance tests in Iberian and Landrace pigs | J. M. Rodríguez-López, M. Lachica, L. González-Valero, I. Fernández-Fígares | <p>As insulin sensitivity may help to explain divergences in growth and body composition between native and modern breeds, metabolic responses to glucose infusion were measured using an intra-arterial glucose tolerance test (IAGTT). Iberian (n = 4... |  | Monogastrics, Physiology, Pig nutrition | Jordi Estellé | 2019-12-28 10:51:03 | View | |
24 Mar 2023
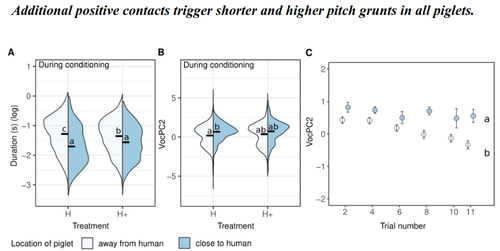
The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationshipAvelyne S Villain, Carole Guérin, Céline Tallet https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.15.484457Qualitative aspects of grunts vary with pigs' mental statesRecommended by Isabelle Veissier based on reviews by Matteo Chincarini and 1 anonymous reviewerVillain et al., (2023) investigated the structure of vocalisations in piglets in relation to human-animal-relationship. They first established a positive relationship by habituating piglets to be positively handled at weaning or later on after weaning. They then compared the reactions of piglets previously positively handled at weaning to that of non-handled piglets during tests in presence of a human (interacting or not), and also before and after the conditioning period when all piglets received positive contacts. They showed that the duration and frequency of grunts emitted in the presence of the human depends on previous contacts. More specifically, grunts are shorter and higher pitched in pigs that have been positively handled, in line with a positive human-animal relationship which is also observed through proximity of the piglets with the human. The authors concluded that the structure of pig vocalisation can reflect the quality of their relationship with humans. The authors also showed that not only the response to humans is modified by positive contacts but also the general mood of piglets, with piglets positively handled at weaning emitting shorter grunts than non-handled piglets, whatever the context. Another interesting finding is the temporality of behaviour of pigs habituated to positive contacts: during the first tests, they stay close to the human, probably being reassured by the proximity of the human. Then, when tests are repeated, they explore more the test room, using the human as an exploratory basis as already reported in the literature. The hypotheses of the study are clear. The methods are reported in details so that the work is reproducible. The interpretation of results is sound. The manuscript is clearly written. This paper brings new and original knowledge in the field of animals’ emotional responses and human-animal relationship: on the structure of grunts in relation to positive affects (positive emotion, positive mood) and on the temporality of the responses to human presence. I recommend this manuscript for its originality and quality. Isabelle Veissier Villain, A.S., Guérin, C., Tallet, C., 2023. The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationship. bioRxiv 2022.03.15.484457, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.15.484457 | The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationship | Avelyne S Villain, Carole Guérin, Céline Tallet | <p>Studying human-animal interactions in domestic species and how they affect the establishment of a positive Human-Animal Relationship (HAR) may help us improve animal welfare and better understand the evolution of interspecific interactions asso... |  | Animal behaviour , Animal cognition, Animal welfare | Isabelle Veissier | 2022-03-23 09:34:45 | View | |
09 Apr 2022
The impact of housing conditions on porcine mesenchymal stromal/stem cell populations differ between adipose tissue and skeletal muscleAudrey Quéméner, Frédéric Dessauge, Marie-Hélène Perruchot, Nathalie Le Floc’h, Isabelle Louveau https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.08.447546Housing conditions affect cell populations in adipose and muscle tissues of pigsRecommended by Hervé Acloque based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThe adaptability of livestock to changing environments is based in particular on their genetic characteristics but also on the farming conditions to which they are subjected. However, this last point is poorly documented and little is known about its contribution to environmental challenges. The study by Quéméner and colleagues [1] addresses this question by assessing the effect of two hygiene conditions (good vs poor) on the distribution of cell populations present in adipose and muscle tissues of pigs divergently selected for feed efficiency [2]. The working hypothesis is that degraded housing conditions would be at the origin of an hyper stimulation of the immune system that can influence the homeostasis of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle and consequently modulate the cellular content of these tissues. Cellular compositions are thus interesting intermediate phenotypes for quantifying complex traits. The study uses pigs divergently selected for residual feed intake (RFI+ and RFI-) to assess whether there is a genetic effect associated with the observed phenotypes. The study characterized different stromal cell populations based on the expression of surface markers: CD45 to separate hematopoietic lineages and markers associated with the stem properties of mesenchymal cells: CD56, CD34, CD38 and CD140a. The authors observed that certain subpopulations are differentially enriched according to the hygiene condition (good vs poor) in adipose and skeletal tissue (CD45-CD56-) sometimes with an associated (genetic) lineage effect. This pioneering study validates a number of tools for characterizing cell subpopulations present in porcine adipose and muscle tissue. It confirms that housing conditions can have an effect on intermediate phenotypes such as intra-tissue cell populations. This pioneering work will pave the way to better understand the effects of livestock systems on tissue biology and animal phenotypes and to characterize the nature and function of progenitor cells present in muscle and adipose tissue. [1] Quéméner A, Dessauge F, Perruchot MH, Le Floc’h N, Louveau I. 2022. The impact of housing conditions on porcine mesenchymal stromal/stem cell populations differ between adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. bioRxiv 2021.06.08.447546, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.08.447546 [2] Gilbert H, Bidanel J-P, Gruand J, Caritez J-C, Billon Y, Guillouet P, Lagant H, Noblet J, Sellier P. 2007. Genetic parameters for residual feed intake in growing pigs, with emphasis on genetic relationships with carcass and meat quality traits. Journal of Animal Science 85:3182–3188. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2006-590. | The impact of housing conditions on porcine mesenchymal stromal/stem cell populations differ between adipose tissue and skeletal muscle | Audrey Quéméner, Frédéric Dessauge, Marie-Hélène Perruchot, Nathalie Le Floc’h, Isabelle Louveau | <p><strong>Background.</strong> In pigs, the ratio between lean mass and fat mass in the carcass determines production efficiency and is strongly influenced by the number and size of cells in tissues. During growth, the increase in the number of c... |  | Monogastrics, Physiology, Veterinary science | Hervé Acloque | 2021-06-08 17:34:54 | View | |
23 Aug 2023
Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution?Birte L. Nielsen, Huw D.R. Golledge, Jen-Yun Chou, Irene Camerlink, Péter Pongrácz, Maria Camila Ceballos, Alexandra L. Whittaker and I. Anna S. Olsson https://www.doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/s6459Can a consensus be reached on the ethical review of animal experimentation for livestock species?Recommended by Hervé Acloque based on reviews by Christian Nawroth, Patrick Gonin and Leon borgdorf"Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution?" by Birte Nielsen and colleagues [1] provides food for thought on the ethical assessment of experiments involving farm animals. While regulations can provide a precise framework, they differ from country to country and do not consider several cases, mainly when the experimentation involves non- or minimally invasive manipulations. It is also the case when research projects use farmed animals that do not fall within the scope of the regulations on animal experimentation but have undergone practices that can be authorised on farms but may raise ethical questions (tail docking, live castration, tooth filing, beak trimming, dehorning). On the other hand, the heterogeneity of the criteria taken into account by the ethics committees, when they exist (and this can differ greatly from one country to another), do not necessarily correspond to the criteria of the journals, the reviewers and the bodies brought in to evaluate the research project, or to the regulations specific to each country. All these paradoxes lead the authors to propose solutions, the most straightforward and spontaneous of which is to ask ourselves questions about this issue upstream of the experimental design required to answer a given scientific question. While increasing the number of ethical review committees may be an insufficient option, the authors insist on the importance of improving committee members' training, taking into consideration jurisdictions' differences between countries and spending more time on ethics evaluation during manuscripts' reviewing. In addition, the upstream assessment of research projects by ethics committees, specific to an institution (research institute, universities, companies), a scientific publisher or even a dedicated international ethical review board may also be a good option. The ethical evaluation of research projects is a question at the heart of our research activities, for which we do not have all the answers. As with scientific reviewing, we must take on the role of evaluator or be evaluated ourselves, using criteria and feelings that are not always consensual. The heterogeneity of evaluation systems within the scientific community, the lack of training for scientists in the fundamentals of ethical evaluation, and the different perceptions of the animal condition between countries and cultures can lead to a reciprocal lack of understanding between evaluator and evaluated, and sometimes a feeling of injustice, as some research may be easy to conduct in one country but difficult in another. Indeed, it is exciting to read the exchanges between the authors and the three reviewers who assessed this opinion paper to appreciate the diversity of points of view and see specific points of divergence. In addition to animal experimentation, the judgment handed down on 30 June 2023 by the French court penalising a pig farmer for the abusive use of an authorised breeding practice (tail docking) is a perfect illustration of the fact that the ethical assessment of practices and handling of farm animals now extends far beyond the scientific world and is becoming an increasingly important factor in the relationship between society and animal breeding. Failure to consider this evolution, whether in experimentation or animal husbandry, may have legal consequences and increase the lack of understanding between our practices and how society perceives them. The questions raised and the solutions proposed in the article by Nielsen et al. are central to our concerns, not only for the scientific community but also to meet the expectations of all stakeholders. Finally, although the authors do not directly address the question of genome editing and research using edited farm animals, this is and will be at the heart of future issues concerning the ethical evaluation of research projects. As with practices and manipulations, the intentionality of the modifications induced leads us to question and evaluate, in farmed species, their consequences on animal welfare and their relevance to society and the development of more sustainable and socially accepted animal husbandry. Reference [1] Nielsen, B. L., Golledge, H. D. R., Chou, J., Camerlink, I., Pongrácz, P., Ceballos, M., Whittaker, A. L., Olsson, I. S. (2023) Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution? OSF Preprints. Ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/s6459 | Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution? | Birte L. Nielsen, Huw D.R. Golledge, Jen-Yun Chou, Irene Camerlink, Péter Pongrácz, Maria Camila Ceballos, Alexandra L. Whittaker and I. Anna S. Olsson | <p>As the article is a short Opinion Paper, it has no abstract, but it aims to highlight the inherent challenges to ethics review of animal (welfare) science research, especially the differences between different countries and jurisdictions which ... |  | Animal behaviour , Animal welfare, Open science, Veterinary science | Hervé Acloque | 2023-05-05 13:27:22 | View | |
05 Jul 2022
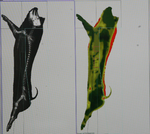
Impact of pre-breeding feeding practices on rabbit mammary gland development at mid-pregnancy.Cathy Hue-Beauvais, Karine Bebin, Raphael Robert, Delphine Gardan-Salmon, Mickael Maupin, Nicolas Brun, Etienne Aujean, Florence Jaffrezic, Steve Simon, Madia Charlier, Fabienne Le Provost https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.17.476562Managing the feeding of rabbits to improve metabolic efficiencyRecommended by Giuseppe Conte based on reviews by Marion Boutinaud, Davi Savietto and 1 anonymous reviewerA correct execution of feeding plan for growing rabbit decreases the possibility of post-weaning digestive disorders, thus enhancing the feed efficiency in the animals. However, a limitation of feed daily quantity is required between 10 weeks of age and the first artificial insemination. This limitation causes energy deficiency with a consequent reduction in fertility. Beauvais et al. (2022) studied the impact of feed restriction strategies in female rabbits. Four feed restriction strategies were applied in two distinct periods (post-weaning and puberty) and evaluated by different physiological parameters (growth rate, metabolic profiles, reproductive parameters and mammary gland development). In the first part of the paper, the authors evaluated the association between weight slopes and feeding strategies in the late post-weaning and peripartum period in the four groups. As revealed by the authors, a significant difference was observed during the late post-weaning period, which remained significant between the pubertal and fattening phases. Probably these differences are related to the restriction feeding pattern. The results indicated that restrictive feeding changes in the first step of post-weaning period is associated with a significant difference in body weight. This difference occurs from the third week of diet, highlighting the high sensitivity of growing rabbit to nutrition during the post-weaning period. In the second part of the paper, the authors evaluated the expression of genes involved in the lipid metabolism. During the mid-pregnancy, was revealed a significant higher expression of lipogenic genes, which may be considered as useful markers for the mammary epithelial development in less restrictive strategies during early life period. The results proposed by Beauvais et al. (2022) enlighten the important role played by the feeding conditions of young female rabbits in the early life rearing. In particular, this activity provides specific recommendations for optimizing lactation and thus preventing neonatal mortality of the offspring. Moreover, the authors provide indications about the effect of feeding strategies on the mammary development and gene expression with absolute consequences on the development of offspring. Mammary lipid metabolism affects the milk profile and therefore the growth performance of the young animals. Reference
Hue-Beauvais C, Bebin K, Robert R, Gardan-Salmon D, Maupin M, Brun N, Aujean E, Jaffrezic F, Simon S, Charlier M, Le Provost F (2022). Impact of pre-breeding feeding practices on rabbit mammary gland development at mid-pregnancy. biorXiv, 2022.01.17.476562, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.17.476562 | Impact of pre-breeding feeding practices on rabbit mammary gland development at mid-pregnancy. | Cathy Hue-Beauvais, Karine Bebin, Raphael Robert, Delphine Gardan-Salmon, Mickael Maupin, Nicolas Brun, Etienne Aujean, Florence Jaffrezic, Steve Simon, Madia Charlier, Fabienne Le Provost | <p>Optimizing rabbit does preparation during early life to improve reproductive potential is a major challenge for breeders. Does selected for reproduction have specific nutritional needs, which may not be supplied with the common practice of feed... |  | Animal nutrition modelling | Giuseppe Conte | 2022-01-19 14:44:30 | View | |
15 Dec 2020
Accuracy of predicting chemical body composition of growing pigs using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometryClaudia Kasper, Patrick Schlegel, Isabel Ruiz-Ascacibar, Peter Stoll, Giuseppe Bee https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.15.286153Accurate predictions of chemical composition of pigs for a wide range of body weights: no longer a myth!Recommended by Florence Gondret based on reviews by Mathieu Monziols and 1 anonymous reviewerAssessing body or carcass composition in growing pigs is essential to refine nutritional models, select for specific traits and evaluate pork products. The gold standard methods are dissection and chemical measurements, which are time-consuming and invasive ways to obtain the data. Different teams have tested dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), especially for determining total and regional body composition of fat, soft lean tissues and bone minerals [1-3]. The DEXA measurements are quick, non-invasive, precise, and operator independent. However, the instruments from different manufacturers are unique in implementation so that it is difficult to obtain and share generalized equations. In addition, the validity and accuracy of the measures when applied to pigs having very different composition have been scarcely addressed.
The present manuscript shows that carcass analysis by DEXA can be used to predict empty body chemical composition, and it provides accuracy values for the content in single nutrients (protein, lipids, Ca, P). The body weight range used to generate differences in body composition is very large (20 to 100 kg), which is important when studying pigs along growth. Moreover, regression equations within weight classes (20, 60 and 100 kg) show no important biases, with the exception for body fat especially at the earliest growth stages. Limitations of the technique are the needs of anesthesia when applied to living pigs, and of standardizing the positions of body, carcass and cuts when applied to living or dissected pigs. Another originality of the manuscript is the comparison of the obtained calibrations with previously published prediction models, showing that the differences do not preclude the possibility to use a single model when built from a meta-analysis of the different data. Taken together, this work offers good perspectives to refine nutritional models by inputs from rapidly analyzed body chemical composition and to monitor body and carcass composition in several pigs for genetics applications.
References [1] Mitchell AD., Scholz AM., Pursel VG., and Evock-Clover CM. (1998). Composition analysis of pork carcasses by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Journal of Animal Science. 76(8), 2104-14. https://doi.org/10.2527/1998.7682104x [2] Marcoux M., Bernier JF., and Pomar C. (2003). Estimation of Canadian and European lean yields and composition of pig carcasses by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Meat Science. 63(3), 359-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1740(02)00094-3 [3] Kipper M., Marcoux M., Andretta I., and Pomar C. (2018). Repeatability and reproducibility of measurements obtained by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry on pig carcasses. Journal of Animal Science, 96(5), 2027-2037. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skx046 " | Accuracy of predicting chemical body composition of growing pigs using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry | Claudia Kasper, Patrick Schlegel, Isabel Ruiz-Ascacibar, Peter Stoll, Giuseppe Bee | <p>Studies in animal science assessing nutrient and energy efficiency or determining nutrient requirements necessitate gathering exact measurements of body composition or body nutrient contents. Wet chemical analysis methods or standardized dissec... |  | Agricultural sustainability, Animal nutrition modelling, Monogastrics, Physiology, Pig nutrition | Florence Gondret | 2020-09-17 10:44:58 | View | |
10 Aug 2022

Decreasing the level of hemicelluloses in sow's lactation diet affects the milk composition and post-weaning performance of low birthweight piglets.Francesco Palumbo, Giuseppe Bee, Paolo Trevisi, Marion Girard https://doi.org/10.31220/agriRxiv.2022.00116Varying the hemicellulose content in the diet of lactating sows highlights the importance of early-life interventions for improving health and performance of small piglets during the post-weaning periodRecommended by Florence Gondret based on reviews by Hélène Quesnel and Myriam GrundyOne of the key questions in pig industry nowadays is how health and performance of piglets can be improved by sow nutrition and milk composition. The levels of dietary fibers in sow’s gestation diet have positive effects observed on the litters. However, the composition of dietary fibers and the organization of polysaccharides within the cell wall in the different plants determine their physicochemical properties and, thereby, their behaviour in the gut of the sows and the subsequent physiological response of the animals. Hemicelluloses are polysaccharides constituents of the cell walls of plants, which are fermented in the gut to produce volatile fatty acids (VFA). These VFA can serve as energy source for milk synthesis and can thereby influence the development of suckling piglets. Palumbo and colleagues (1) proposed an original experimental design to compare diets with similar fiber contents but different hemicellulose levels, thanks to varying the sources of fibers used in the dietary formulations. Effects were studied on performance and health of lactating sows and their piglets during suckling period and until post-weaning. The dietary treatments had no effect on the total number of piglets weaned and, consequently, on litter weight at weaning. Milk yield was not influenced by the dietary treatments, but milk composition (lactose content, copper and threonine proportions) was affected by the level of hemicellulose in the maternal diets. With a decreasing hemicellulose level in sow diet, milk lactose content linearly decreased, whereas the copper and threonine contents linearly increased. There was no effect on piglet performance during the lactation period. During the second week of post-weaning, a quadratic increase in the incidence of diarrhoea and the number of days with diarrhoea for suckling piglets was observed with decreasing hemicellulose level in diet. Interestingly, the observed effects were partly different for piglets born with a low body weight. Indeed, there was a linear decrease in the incidence of diarrhoea and days with diarrhoea with decreased hemicellulose level in the maternal diet for those piglets, together with increased growth performance from birth to two weeks post-weaning. The authors postulated that the improved growth performance and the lower incidence of diarrhoea observed in small piglets during post-weaning period may be related to the increased abundance of threonine and copper and increased concentration of total VFA in milk of sows fed a diet with reduced hemicellulose levels. This study confirms the importance of early-life interventions to improve the post-weaning development and health of this sub-population of piglets. Reference (1) Palumbo F, Bee G, Trevisi P, and Girard M. (2022). Decreasing the level of hemicelluloses in sow's lactation diet affects the milk composition and post-weaning performance of low birthweight piglets. agriRxiv 2022.00116, ver 4 (R3), peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.31220/agriRxiv.2022.00116 | Decreasing the level of hemicelluloses in sow's lactation diet affects the milk composition and post-weaning performance of low birthweight piglets. | Francesco Palumbo, Giuseppe Bee, Paolo Trevisi, Marion Girard | <p>Hemicelluloses (HC) are polysaccharides constituents of the cell walls of plants. They are fermented in the gut to produce volatile fatty acids (VFA). The present study investigated the effects of decreasing HC level in sow's lactation diet on ... |  | Pig nutrition | Florence Gondret | 2022-01-21 12:00:22 | View | |
15 Feb 2024

On-farm hatching and contact with adult hen post hatch induce sex-dependent effects on performance, health and robustness in broiler chickensL. A. Guilloteau, A. Bertin, S. Crochet, C. Bagnard, A. Hondelatte, L. Ravon, C. Schouler, K. Germain, A. Collin https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.17.541117The hen, the egg and the chick in conventional and on-farm hatching systemsRecommended by Florence Gondret based on reviews by Nicolas Bedere and Anna OlssonTo limit the use of antibiotics in the few days after hatching, it is necessary to improve the robustness of chicks during the early post-hatch period. This can be achieved by ensuring immediate access to feeds, optimizing the implantation and maturation of the microbiota and immune system of each chick, and minimizing exposure of stressors such as transportation. The study conducted by Guilloteau and colleagues (2024) compared the performance and health of chicks raised in conventional hatching systems with those raised in on-farm hatching systems. The authors showed that both systems yielded similar hatching percentage of eggs. Chicks from on-farm hatching systems exhibited higher body weights during the post-hatch period compared to those from conventional hatching, whereas health parameters were not affected by the system. An originality of the study was the examination of the benefits of the presence of an adult hen in hatching systems. The effects on chick traits were interpreted in relation to the hen behavior at hatching and a classification according to maternal or agonistic activities towards the chicks. However, the experimental design did not allow to make statistical correlations between hen behavior pattern and chick traits. Importantly, the presence of a hen decreased the hatching percentage, and this was likely associated with hen aggressiveness in the pen. The presence of the hen deteriorated the quality scores of the chicks in the on-farm hatching system, and increased mortality of chicks at hatching, negatively impacting chick weight gain and feed efficiency during the few days after hatching in both conventional and on-farm hatching systems. Thereafter, the effect of the presence of a hen on chick body weight was different according to the sex of the chicks and the type of hatching system. The presence of a hen did not reduce the parasitic load of the chicks nor improved clinical signs. No specific characterization of the fecal microbiota of the chicks was conducted, preventing the testing whether or not the presence of the hen affected the early implantation and maturation of the chick microbiome. Altogether, the data indicate that on-farm hatching systems are at least equivalent (in terms of health traits, feed efficiency) or even favorable (for faster growth in the early period after hatching) for chicks. Training the hens (considered as foster adults) to the presence of eggs and chicks or selecting hens according to specific activity behavioral patterns could be ways to establish better interactions between hens and chicks. Although the number and type of environmental stressors tested in the experiment differ from those in commercial farms, the article opens new perspectives for alternative hatching and farming practices. Reference Guilloteau LA, Bertin A, Crochet S, Bagnard C, Hondelatte A, Ravon L, Schouler C, Germain K, Collin A (2024) On-farm hatching and contact with adult hen post hatch induce sex-dependent effects on performance, health and robustness in broiler chickens. bioRxiv, 2023.05.17.541117. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.17.541117.
| On-farm hatching and contact with adult hen post hatch induce sex-dependent effects on performance, health and robustness in broiler chickens | L. A. Guilloteau, A. Bertin, S. Crochet, C. Bagnard, A. Hondelatte, L. Ravon, C. Schouler, K. Germain, A. Collin | <p>To improve the early perinatal conditions of broiler chicks, alternative hatching systems have been developed. On-farm hatching (OFH) with an enriched microbial and stimulating environment by the presence of an adult hen is a promising solution... |  | Animal welfare, Farming systems, Poultry, Veterinary science | Florence Gondret | 2023-05-31 12:56:47 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Karol B Barragán-Fonseca
Mohammed Gagaoua
Rachel Gervais
Florence Gondret
Francois Meurens
Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo
Anna Olsson
Seyed Abbas Rafat
Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas









