Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * ▲ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
03 Apr 2025

A pipeline with pre-processing options to detect behaviour from accelerometer data using Machine Learning tested on dairy goats.Sarah Mauny, Joon Kwon, Nicolas C. Friggens, Christine Duvaux-Ponter, Masoomeh Taghipoor https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.12627197Introducing a feature extraction method and implementing a gradient boosting algorithm to predict behavioral traits in animalsRecommended by Seyed Abbas Rafat based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In the livestock industry, the concerns of society and livestock farmers have changed in recent decades, moving from a focus solely on production traits to sustainable production while respecting animal welfare (Ducrot et al., 2024). Animal behavior parameters can serve as a reliable proxy for animal welfare, but collecting large data sets of behavioral data on farm is very time-consuming when not automatized. Accelerometers are promising devices to detect animal behavior. A key element of the efficiency of the prediction of animal behavior from accelerometer data is the adequacy of pre-processing methods (Riaboff et al., 2019,Riaboff et al., 2022, Vidal et al., 2023). The article of Mauny et al., (2025) aims to find a solution for using huge automatized data. So, livestock farmers can effectively use new technologies to monitor animal behavior and then correct poor husbandry routines. Authors used the pipeline ACT4Behav - (Accelerometer-based Classification Tool for identifying Behaviours) - (Mauny et al., 2024) for the pre-processing of accelerometer data with the aim of selecting the most important features of dairy goats related to rumination, head in the feeder, lying and standing (using data based on video recordings for the validation of behavior activity). Mauny et al., (2025) established a clear methodology that systematically obtain the best features and processing techniques to predict each targeted variable from raw accelerometer data. The work provides valuable information for both animal husbandry specialists and data mining scientists. The main limitation of the work is the small number of animals for both training and model testing. References Ducrot C, Barrio MB, Boissy A, Charrier F, Even S, Mormède P, Petit S, Pinard-van der laan M-H, Schelcher F, Casabianca F, Ducos A, Foucras G, Guatteo R, Peyraud J-L, Vayssier-Taussat M, Veysset P, Friggens NC and Fernandez X. 2024. Animal board invited review: Improving animal health and welfare in the transition of livestock farming systems: Towards social acceptability and sustainability. animal 18, 101100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.animal.2024.101100 Mauny, S, Kwon J, Friggens NC, Duvaux-Ponter C, Taghipoor M. 2024. ACT4Behav (Accelerometer-based Classification Tool for identifying Behaviours): a Machine Learning pipeline with extensive pre-processing and feature creation options. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.12624796 Mauny S, Kwon J, Friggens NC, Duvaux-Ponter C, Taghipoor M. 2025. A pipeline with pre-processing options to detect behaviour from accelerometer data using Machine Learning tested on dairy goats.. Zenodo, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.12627197 Riaboff L, Aubin S, Bédère N, Couvreur S, Madouasse A, Goumand E, Chauvin A, Plantier G. 2019. Evaluation of pre-processing methods for the prediction of cattle behaviour from accelerometer data. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 165, 104961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2019.104961 Riaboff L, Shalloo L, Smeaton AF, Couvreur S, Madouasse A, Keane MT. 2022. Predicting livestock behaviour using accelerometers: A systematic review of processing techniques for ruminant behaviour prediction from raw accelerometer data. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 192, 106610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.106610 Vidal G, Sharpnack J, Pinedo P, Tsai IC, Lee AR, Martínez-López B. 2023. Impact of sensor data pre-processing strategies and selection of machine learning algorithm on the prediction of metritis events in dairy cattle. Preventive Veterinary Medicine 215, 105903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2023.105903
| A pipeline with pre-processing options to detect behaviour from accelerometer data using Machine Learning tested on dairy goats. | Sarah Mauny, Joon Kwon, Nicolas C. Friggens, Christine Duvaux-Ponter, Masoomeh Taghipoor | <p style="text-align: justify;">Animal behaviour is a significant component in the evaluation of animal welfare. Conducting continuous observations of animal behaviour is a time-consuming task and may not be feasible over extended periods for all ... |  | Animal behaviour , Animal welfare, Precision livestock farming, Small ruminants | Seyed Abbas Rafat | 2024-07-04 12:45:42 | View | |
01 Sep 2022

Detecting dairy cows' lying behaviour using noisy 3D ultrawide band positioning dataI. Adriaens, W. Ouweltjes, M. Pastell, E. Ellen, C. Kamphuis https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6627251A novel method to monitor lying behaviour of dairy cows by combining noisy spatial positioning data, time-series segmentation based on statistical changepoints and machine learning classification algorithmRecommended by Eliel Gonzalez-Garcia based on reviews by Kareemah Chopra and John Fredy Ramirez AgudeloUsing on-farm sensors in dairy farming is known to help decision makings and farmer objectives in the monitoring and potential improvement of animal behaviour, health and production performance. However, in indoor positioning systems, data interpretation is complicated by the inaccuracy and noise in the time series, missing data caused not only by sensor failure or the harsh and changing farm environments in which they operate, but also by the animals' specific physiology itself. Thus, working with spatial data has proven challenging mainly due to their enormous heteroscedasticity, which depends on multiple factors such as the cow, the time of the day, the behaviour, factors interfering with the sensor system, etc., for which we cannot account mathematically. Applying purely black-box approaches generally results in insufficient robustness, interpretability and generalisability. With this work, Adriaens et al. (2022) developed a relatively simple and new methodology to monitor the lying behaviour of dairy cows by using noisy spatial positioning data, while combining time-series segmentation based on statistical changepoints and a machine learning classification algorithm. The two-step methodology identifies lying behaviour using an ultra-wide band indoor positioning system. Getting-up or lying-down events were indicated by the accelerometers. Overall classification and lying behaviour prediction performance was above 91% in independent test sets, with a very high consistency across cow-days. The robustness of the algorithm was demonstrated by the fact that both the cow identity-based split and the time-based split performed equally well. The article represents an original contribution for advancing the state of the art in the automated quantification of lying behaviour in dairy cows, aiming to monitor health or animal welfare issues. Future research must be considered however to validate the performance of the model when using different position-measuring technologies, in other farm settings and over a longer period of time.
Reference Adriaens I, Ouweltjes W, Pastell M, Ellen E, Kamphuis C. 2022. Detecting dairy cows' lying behaviour using noisy 3D ultra-wide band positioning data. Zenodo, 6627251, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6627251
| Detecting dairy cows' lying behaviour using noisy 3D ultrawide band positioning data | I. Adriaens, W. Ouweltjes, M. Pastell, E. Ellen, C. Kamphuis | <p>In precision livestock farming, technology-based solutions are used to monitor and manage<br>livestock and support decisions based on on-farm available data. In this study, we developed<br>a methodology to monitor the lying behaviour of dairy c... |  | Animal behaviour , Mathematical modelling, Precision livestock farming | Eliel Gonzalez-Garcia | 2022-02-28 18:19:37 | View | |
06 Jan 2025
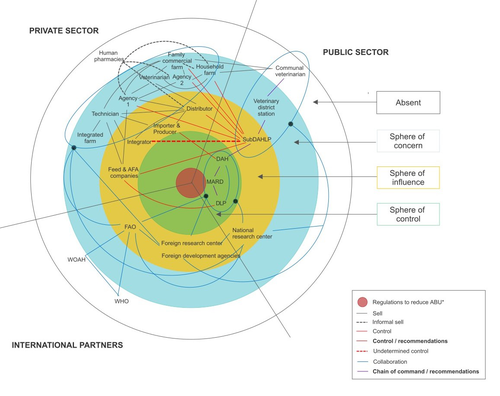
Understanding the implementation of antimicrobial resistance policies in Vietnam: a multilayer analysis of the veterinary drug value chainChloé Bâtie, Nguyen Van Duy, Nguyen Thi Minh Khue, Marisa Peyre, Marion Bordier, Nguyen Thi Dien, Vu Dinh Ton, Flavie Goutard https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.27.24309573Bridging the gap in antibiotic regulation within Vietnam's livestock sectorRecommended by François Meurens based on reviews by Rebecca Hibbard and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Rebecca Hibbard and 1 anonymous reviewer
The reduction of antibiotic use in livestock production, for the different species, has become a critical focus in national action plans across many countries, underscoring the urgent need to tackle this issue to preserve public health and combat antibiotic resistance (Xu et al., 2022; Jacobsen et al., 2023; Bava et al., 2024). Among these efforts, Vietnam's ambitious 2017 livestock plan is notable for its comprehensive regulatory framework aimed at controlling antibiotic use. This framework includes a phased ban on prophylactic antibiotics in animal feed and requires mandatory prescriptions for antibiotic access. Despite these promising regulations, their actual implementation poses significant challenges, with limited data available on their practical application. A recent study led by Batie and collaborators attempts to fill this knowledge gap by examining how these regulations are understood, accepted, and applied by stakeholders in the veterinary drug value chain in both northern and southern Vietnam (Batie et al., 2024). The study employed an interesting iterative stakeholder mapping and analysis approach, organizing a focus group in Hanoi with 12 participants and conducting 39 in-depth semi-structured interviews with a diverse range of stakeholders. These included government authorities, national research bodies, international partners, and private sector representatives. The qualitative analysis aimed to map the veterinary drug value chain, assess stakeholders' technical and social capital regarding regulations, and identify key factors influencing regulatory compliance. This research convincingly unveiled a complex network of 30 stakeholder categories and identified ten crucial factors that affect the implementation of regulations. These factors include stakeholders’ perceptions and understanding of the regulations, the availability of technical guidance, economic conflicts of interest, management inconsistencies, and hurdles such as technical and financial constraints, informal distribution channels, international influence, and consumer demand for safety. Additionally, the collective drive to reduce antibiotic resistance emerged as an influential factor. The comprehensive analysis reveals a pressing insight: although Vietnam's regulatory measures are essential for reducing antibiotic usage, their effectiveness is compromised by barriers such as inadequate local stakeholder involvement and various resource limitations. The study emphasizes the necessity for deeper engagement of local stakeholders in developing and refining these regulations. Furthermore, incorporating innovations from small producers into mainstream practices could be vital in overcoming current challenges. Nonetheless, the study acknowledges several limitations. Most interviews were conducted online owing to the health crisis—a much-needed format for time and budget constraints, albeit with some drawbacks such as reduced direct observations and potential information loss (Namey et al., 2019). The sensitivity of the subject may have led participants to withhold their true opinions, although the researchers attempted to mitigate this bias by interviewing multiple respondents from each category and gathering diverse perspectives. Notably, the study struggled to engage informal stakeholders, which could have enriched the description of the informal value chain. Constraints of time and resources meant that only a single representative from some stakeholder categories was interviewed, suggesting that interviewing additional parties, such as another veterinary district station, might have clarified roles within the drug value chain. The stakeholder identification was initially influenced by the researchers’ familiarity with the Vietnamese context; however, the iterative process helped address this limitation by recruiting new participants based on existing participants' knowledge. Additionally, translation issues may have introduced misunderstandings, potentially leading to an incomplete representation of the veterinary drug value chain, which reflects the situation as of data collection in 2021. For Vietnam to meet its policy objectives and contribute to the global endeavor against antibiotic resistance, it is crucial to reconcile stakeholder discrepancies and promote collaborative innovation. By fostering an inclusive environment for all parties, Vietnam can not only enhance regulatory adherence but also strengthen its commitment to sustainable and responsible livestock farming practices. The study is thoughtfully designed and skillfully executed. Additionally, the authors have made further improvements based on feedback from the journal. Readers will find the article both informative and engaging, providing valuable insights. I highly recommend this original article on the regulatory framework for controlling antibiotic use in Vietnam's livestock production systems. References Batie, C., Duy, N. V., Khue, N. T. M., Peyre, M., Bordier, M., Dien, N. T., et al. (2024). Understanding the implementation of antimicrobial resistance policies in Vietnam: a multilayer analysis of the veterinary drug value chain. medRxiv, 2024.06.27.24309573, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.27.24309573 Bava, R., Castagna, F., Lupia, C., Poerio, G., Liguori, G., Lombardi, R., et al. (2024). Antimicrobial Resistance in Livestock: A Serious Threat to Public Health. Antibiotics 13, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13060551 Jacobsen, A. B. J. E., Ogden, J., and Ekiri, A. B. (2023). Antimicrobial resistance interventions in the animal sector: scoping review. Front. Antibiot. 2. https://doi.org/10.3389/frabi.2023.1233698 Namey, E., Guest, G., O’Regan, A., Godwin, C. L., Taylor, J., and Martinez, A. (2019). How Does Mode of Qualitative Data Collection Affect Data and Cost? Findings from a Quasi-experimental Study. Field Methods. https://doi.org/10.1177/1525822X19886839 Xu, C., Kong, L., Gao, H., Cheng, X., and Wang, X. (2022). A Review of Current Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics in Food Animals. Front Microbiol 13, 822689. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.822689
| Understanding the implementation of antimicrobial resistance policies in Vietnam: a multilayer analysis of the veterinary drug value chain | Chloé Bâtie, Nguyen Van Duy, Nguyen Thi Minh Khue, Marisa Peyre, Marion Bordier, Nguyen Thi Dien, Vu Dinh Ton, Flavie Goutard | <p>Reducing antibiotic use in livestock production has been a target for national action plans worldwide. The Vietnamese livestock plan issued in 2017 has, among other objectives, strengthened the regulatory framework for antibiotic use. While a p... |  | Animal epidemiology, Animal health, Farming systems, Veterinary epidemiology , Veterinary science | François Meurens | 2024-07-15 10:47:33 | View | |
09 Feb 2024
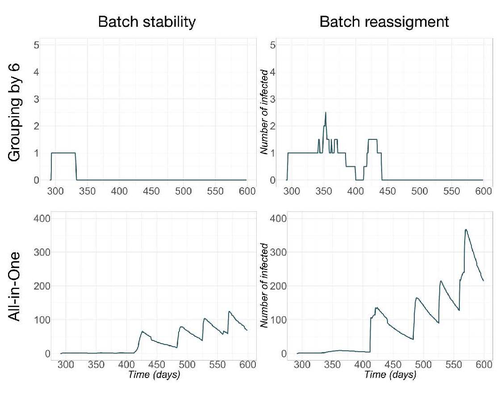
Pig herd management and infection transmission dynamics: a challenge for modellers.Vianney Sicard, Sébastien Picault, Mathieu Andraud https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.17.541128Towards models of infection transmission dynamicsRecommended by Marie-Pierre Letourneau Montminy based on reviews by Gustavo Machado and 1 anonymous reviewerEpidemics such as PRRSv-like virus in pig farms has tremendous impact on the competitiveness of swine production. However, its control requires an understanding of the complex interaction between pathogen transmission, disease impact, population dynamics and management. By using mechanistic epidemiological modelling, Sicard et al. (2023) open up a very interesting field of possibilities. This article describes work aimed at assessing the consequences of infections, taking into account the interaction between clinical outcomes and population dynamics. This study shows how this interaction can influence transmission dynamics at the herd level. It highlights the need to further explore this direction, integrating both disease impacts in breeding practices and structural changes in population dynamics, such as pig crossbreeding and grouping methodologies. Reference Sicard V, Picault S, Andraud M (2023) Pig herd management and infection transmission dynamics: a challenge for modellers. bioRxiv, 2023.05.17.541128. ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.17.541128
| Pig herd management and infection transmission dynamics: a challenge for modellers. | Vianney Sicard, Sébastien Picault, Mathieu Andraud | <p>The control of epidemics requires a thorough understanding of the complex interactions between pathogen transmission, disease impact, and population dynamics and management. Mechanistic epidemiological modelling is an effective way to address t... |  | Animal epidemiology modelling, Animal health, Bioinformatics, Farming systems, Infectious diseases, Mathematical modelling, Open science, Population dynamics, Veterinary epidemiology | Marie-Pierre Letourneau Montminy | 2023-05-22 15:07:37 | View | |
29 Jan 2024
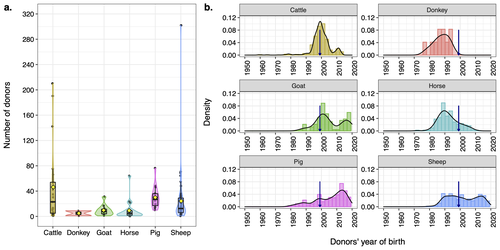
Assessing the potential of germplasm collections for the management of genetic diversity: the case of the French National CryobankAlicia Jacques, Delphine Duclos, Coralie Danchin-Burge, Marie-Jose Mercat, Michele Tixier-Boichard, Gwendal Restoux https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.19.549644Exploring Genetic Diversity Management: Unveiling the Potential of Germplasm Collections in the French National CryobankRecommended by Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas based on reviews by Roy Costilla and 1 anonymous reviewerThe study by Jacques et al. (2024) addresses a critical concern in the context of genetic diversity erosion in domesticated animal populations. The research uses data from the cryopreserved resources from the French National Cryobank to manage genetic diversity in livestock species. The authors employ a comprehensive methodology to propose novel biodiversity metrics to characterize the status of genetic diversity of cryopreserved collections including cattle, sheep, goat, horse, donkey, and pig livestock species. The findings reveal significant variations of genetic diversity at species and breed levels. Breeds with a large commercial distribution had more donors in the collection than local breeds. The authors propose a practical framework for assessing germplasm collections, providing a valuable tool for planning and managing collections at both national and international levels. The study also highlights the usefulness of the Gini-Simpson and effective donor numbers indices to plan a more efficient sampling, whereas the index of diversity impact can be employed in the selection of the most suitable donors for immediate use, based on pedigree but also using genetic markers. In resume, this study makes a significant contribution to the field by offering a framework for the assessment of germplasm collections. Its innovative metrics provide insights that could guide strategic decision-making in planning, managing, and utilizing cryopreserved resources. This research is relevant and can benefit conservationists, and population genetics working towards the preservation and sustainable use of genetic resources in livestock species. Reference Jacques, A., Duclos, D., Danchin-Burge, C., Mercat, M. J., Tixier-Boichard M., Restoux, G. (2024). Assessing the potential of germplasm collections for the management of genetic diversity: the case of the French National Cryobank. bioRxiv 2023.07.19.549644. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.19.549644
| Assessing the potential of germplasm collections for the management of genetic diversity: the case of the French National Cryobank | Alicia Jacques, Delphine Duclos, Coralie Danchin-Burge, Marie-Jose Mercat, Michele Tixier-Boichard, Gwendal Restoux | <p>Through a combination of selective pressure and genetic drift, there has been a notable erosion of genetic diversity in domesticated animal populations. In response, many countries, including France, have developed gene banks in order to conser... |  | Animal genetics | Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas | 2023-07-20 19:08:40 | View | |
20 Dec 2021

Quantifying growth perturbations over the fattening period in swine via mathematical modellingManuel Revilla, Guillaume Lenoir, Loïc Flatres-Grall, Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo, Nicolas C Friggens https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.22.349985An innovative modelling approach to enhance the quality of the quantification of pig resilience during the entire fattening period: Towards an individual pig resilience indexRecommended by Mohammed Gagaoua based on reviews by Arata Hidano, Ludovic Brossard and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Arata Hidano, Ludovic Brossard and 2 anonymous reviewers
The identification of reliable estimates of growth potential and resilience over the fattening period in large populations is a challenge in actual swine breeding conditions. To overcome this drawback, the study by Revilla et al. 2021 in the frame of precision livestock farming aimed to propose an innovative modelling approach, in addition to previous studies from the same group (Revilla et al. 2019), to enhance the quality of the quantification of pig resilience during the entire fattening period. The authors developed a model that quantifies an “individual pig resilience indicator” based on longitudinal data, for instance body weight, recorded routinely by a commercially available automatic feeding system. Revilla and co-workers considered in their study two mainly commercialised pure pig breeds these being Piétrain including Piétrain Français NN Axiom line (Pie NN) free from halothane-sensitivity (ryanodine receptor gene, RYR1) and Piétrain Français Axiom line positive to this gene and Duroc. Therefore, the authors investigated the potential of improving resilience of swine livestock through inclusion for the first time of an “individual pig resilience indicator” in breeding objectives. A database of 13 093 boars (approximately 11.1 million of weightings) belonging to Pie (n= 5 841), Pie NN (n = 5 032) and Duroc (n= 2 220) finished under ad libitum feeding, high sanitary level and controlled temperature was used to develop robust models. The authors checked the three datasets (for each pig breed) independently to explore the variation and gaps (a data pre-treatment procedure) to ensure high quality data for the modelling approach. Then, they applied the Gompertz model and linear interpolation on body weight data to quantify individual deviations from the expected production, allowing the creation of the ABC index. For the modelling, the authors applied a two-step mathematical model approach by first establishing a theoretical growth curve of each animal, while the second step aimed to build the actual perturbed growth curve. The heritability of the index ranged from 0.03 to 0.04, with similar heritability between Piétrain and Duroc breeds. Moreover, moderate genetic relationships were computed between the proposed index and important phenotypic traits in swine production likely BF100: backfat thickness at 100kg; LD100: longissimus dorsi thickness at 100kg; ADG: average daily gain during control and FCR: feed conversion ratio. Developing models able to capture perturbations during the fattening period is a challenge in swine breeding industry. The model and methodology proposed by the authors in this innovative work (although preliminary and with low heritabilities) would help overcome such limit and facilitate a real implementation at large scale in pig breeding system. The modelling approach further offers an opportunity to develop a selection criterion to improve resilience in swine breeding conditions. To explore the full potential of this modelling approach, a larger database and other factors such as breed, behaviour and feeding behaviour of the animals, rearing practices, management and environment conditions, age… etc. are worthy to consider. In the future, more in depth measurements of behaviour that can be computed for example using computer vision should be desirable to increase the robustness of the proposed model. References Revilla, M., Friggens, N.C., Broudiscou, L.P., Lemonnier, G., Blanc, F., Ravon, L., Mercat, M.J., Billon, Y., Rogel-Gaillard, C., Le Floch, N. and Estellé, J. (2019). Towards the quantitative characterisation of piglets’ robustness to weaning: a modelling approach. Animal, 13(11), 2536-2546. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731119000843 Revilla M, Lenoir G, Flatres-Grall L, Muñoz-Tamayo R, Friggens NC (2021). Quantifying growth perturbations over the fattening period in swine via mathematical modelling. bioRxiv, 2020.10.22.349985, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.22.349985 | Quantifying growth perturbations over the fattening period in swine via mathematical modelling | Manuel Revilla, Guillaume Lenoir, Loïc Flatres-Grall, Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo, Nicolas C Friggens | <p>Background: Resilience can be defined as the capacity of animals to cope with short-term perturbations in their environment and return rapidly to their pre-challenge status. In a perspective of precision livestock farming, it is key to create i... |  | Animal genetics, Animal health, Farming systems, Mathematical modelling, Precision livestock farming | Mohammed Gagaoua | 2020-10-26 11:47:08 | View | |
06 Sep 2023
Validation of a Radio frequency identification system for tracking location of laying hens in a quasi-commercial aviary systemSabine G. Gebhardt-Henrich, Alexander Kashev, Matthew B. Petelle, Michael J. Toscano https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.16.528820Tracking large numbers of hens in aviary housing: validation of a Radio Frequency Identification systemRecommended by Anna Olsson based on reviews by Arjen van Putten and Mona Giersberg based on reviews by Arjen van Putten and Mona Giersberg
With the increasing use of cage-free housing systems for laying hens comes the challenge of monitoring the behaviour of individual hens in large enclosures where they can be not only on the floors but on different levels. The aim of the present study by Gebhardt-Henrich et al., (2023) was to validate a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system with the capacity to track a large number of hens for different research and applied purposes where behaviour monitoring is relevant, such as heritability estimates for breeding programs. In a housing system with 225 birds per pens, 26 antennae were placed at different locations. All birds in 5 pens were equipped with a glass tag in a custom-developed leg band. For validation purposes, the behaviour of three hens who could move between two pens was also monitored on video. Equipping these hens with colour-coded backpacks made them identifiable on video. Matching the antennae detection of the focal birds with the behaviour observation showed that the antennae were able to detect a hen on the right tier in > 90% of cases, but that match on antenna level was lower. The limitations of the system are also discussed in this concise methods paper that will be helpful to many researchers interested in tracking laying hens in loose housing systems. Gebhardt-Henrich, S.G., Kashev, A., Petelle, M.B., Toscano, M.J., 2023. Validation of a Radio frequency identification system for tracking location of laying hens in a quasi-commercial aviary system. bioRxiv 2023.02.16.528820. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.16.528820
| Validation of a Radio frequency identification system for tracking location of laying hens in a quasi-commercial aviary system | Sabine G. Gebhardt-Henrich, Alexander Kashev, Matthew B. Petelle, Michael J. Toscano | <p>Cage-free housing is increasingly chosen in Europe, North America, and Australia as an animal-welfare friendly farm system for laying hens. However, hens are kept in large numbers in those systems which makes checking for health and welfare dif... | Animal genetics, Animal welfare | Anna Olsson | 2023-02-17 08:54:51 | View | ||
16 Sep 2024
Cost-efficient assignment panel for ducks. Setup of a cost-efficient assignment panel for duck populations.Chapuis, Hervé, Brard-Fudulea, Sophie, Hazard, Azélie, Vignal, Alain, Demars, Julie, Rouger, Romuald, Teissier, Marc, Gilbert, Hélène https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04542880Providing innovative genetic solutions to the future challenges of the poultry industry: extraction of a small-sized Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) panel using factorial design for parentage assignment in a population consisting of pure and hybrid ducksRecommended by Seyed Abbas Rafat based on reviews by Arash Javanmard and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Arash Javanmard and 2 anonymous reviewers
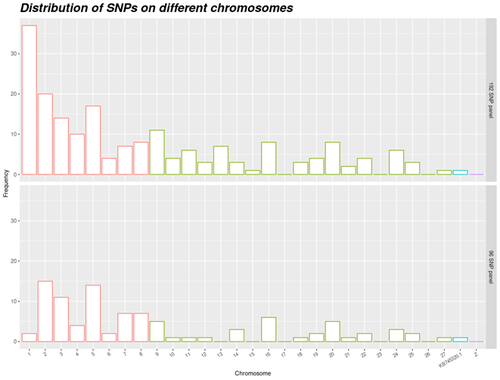
One of the achievements of animal genetics is that it finds solutions along with the emergence of new needs of the animal husbandry community or the adoption of new laws. Muir and Cheng (2013) research serves as a classic example of using the innovations of animal genetics to meet new legal challenges, such as the restriction of beak cutting in laying hens. Muir and Cheng (2013) investigated the genetic diversity to deal with the cannibalism of intact chickens. In 2021, the European Citizens' Initiative urged the European Commission to legislate against the use of cages for farm animals in the livestock industry. Chapuis et al., (2024) presented a successful solution to the poultry industry about this (future) law by presenting a cost-efficient assignment SNP panel. In animal breeding, access to pedigree information is necessary for genetic progress. Since the 1970s, the development of genomic science and molecular techniques has shown their ability in this field. Despite the substantial reduction of genotyping costs in the last 20 years, the practical use of genome-wide genotyping for thousands of SNPs remains challenging. Therefore, the search for a small, cost-effective SNP panel is ongoing, with objectives including genetic diversity (Viale et al., 2017), product traceability (Dominik et al., 2021), species and hybrid identification (Harmoinen et al., 2021) and pedigree construction in wild populations (Ekblom et al., 2021). Furthermore, especially in recent decades, small panels of markers have been proposed for parentage assignment in different animals. For example, Domínguez-Viveros et al., (2020) developed panels with 42 to 63 markers for different sheep breeds in Mexico. Similar panels for parentage assignment have been proposed for salmon (May et al., 2020), rainbow trout (Liu et al., 2016), French sheep (Tortereau et al., 2017), Spanish sheep (Calvo et al., 2021), and European bison (Wehrenberg et al., 2024), with marker numbers of 142, 95, 180, 173, and 96, respectively. Massault et al., (2021) showed by simulation that a panel with at least 50 markers is sufficient for progeny assignment in pearl oysters. These examples highlight that extracting a small panel of markers (usually less than 200) from the total genotyping introduced in different species, can open new horizons for applying genomic information in animal breeding. Chapuis et al. (2024) addressed the challenge of finding an efficient set of markers that can be used in the hybridization of two species of the Pekin duck and the Muscovy duck. They used KASPar technology to setup a panel, with SNPs existing in both species and their hybrids. This panel has sufficient polymorphism to use in practice. Thus, it can be considered as a step forward compared to previous work done on microsatellites. A final list of SNPs was constructed from a reference set comprising 600 K genotyping of Anas platyrhynchos, Cairina moschata and mule duck. In addition to developing of a cost-efficient assignment panel, the work of Chapuis et al. (2024) presented a factorial design to maintain genetic diversity while considering specificities of duck production. The use of factorial design in avian pedigreed populations is relatively novel, making this research particularly innovative. The study's approach to factorial design in populations with limited size may be generalized to similar poultry species. Furthermore, sufficient effective size of population is selected. So, the panel can be used in other populations outside the tested populations. A notable feature of this panel is the use of neutral SNPs, which ensures that markers will not be lost due to future selection pressures over time. The paper of Chapuis et al. (2024) exemplifies the application of molecular genetics to address challenges in the poultry industry. The use of kinship matrix instead of relationship matrix, taking into account the unique characteristics of duck production, could be another novelty of the paper. According to the reviewers' comments, the results can be beneficial in the future, particularly with the introduction of the specific factorial design. References Calvo JH, Serrano M, Tortereau F, Sarto P, Iguacel LP, Jiménez MA, Folch J, Alabart JL, Fabre S and Lahoz B (2021). Development of a SNP parentage assignment panel in some North-Eastern Spanish meat sheep breeds. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research 18, e0406. https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2020184-16805 Chapuis H, Brard-Fudulea S, Hazard A, Vignal A, Demars J, Rouger R, Teissier M, Gilbert H (2024). Cost-efficient assignment panel for ducks. Setup of a cost-efficient assignment panel for duck populations.: An illustration with experimental data. HAL, hal-04542880, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04542880 Domínguez-Viveros J, Rodríguez-Almeida FA, Jahuey-Martínez FJ, Martínez-Quintana JA, Aguilar-Palma GN, Ordoñez-Baquera P (2020). Definition of a SNP panel for paternity testing in ten sheep populations in Mexico, Small Ruminant Research ,193,106262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2020.106262 Dominik S, Duff CJ, Byrne AI, Daetwyler H, Reverter A (2021). Ultra-small SNP panels to uniquely identify individuals in thousands of samples. Animal Production Science 61, 1796–1800. https://doi.org/10.1071/AN21123 Ekblom R, Aronsson M, Elsner-Gearing F, Johansson M, Fountain T, Persson J (2021). Sample identification and pedigree reconstruction in Wolverine (Gulo gulo) using SNP genotyping of non-invasive samples. Conservation Genetics Resources 13, 261–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-021-01208-5 Harmoinen J, von Thaden A, Aspi J, Kvist L, Cocchiararo B, Jarausch A, Gazzola A, Sin T, Lohi H, Hytönen MK, Kojola I, Stronen AV, Caniglia R, Mattucci F, Galaverni M, Godinho R, Ruiz-González A, Randi E, Muñoz-Fuentes V, Nowak C (2021). Reliable wolf-dog hybrid detection in Europe using a reduced SNP panel developed for non-invasively collected samples. BMC Genomics 22, 473. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07761-5 Liu S, Palti Y, Gao G, Rexroad CE (2016). Development and validation of a SNP panel for parentage assignment in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 452, 178–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.11.001 Massault C, Jones DB, Zenger KR, Strugnell JM, Barnard R, Jerry DR (2021). A SNP parentage assignment panel for the silver lipped pearl oyster (Pinctada maxima). Aquaculture Reports 20, 100687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100687 May SA, McKinney GJ, Hilborn R, Hauser L, Naish KA (2020). Power of a dual-use SNP panel for pedigree reconstruction and population assignment. Ecology and Evolution 10, 9522–9531. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.6645 Muir WM, Cheng HW(2013). Genetics and the Behaviour of Chickens: Welfare and Productivity. In Genetics and the Behaviour of Domestic Animals. Vol. 2 (2nd ed.). pp. 1–30.ISBN: 9780128100165 Tortereau F, Moreno CR, Tosser-Klopp G, Servin B, Raoul J (2017). Development of a SNP panel dedicated to parentage assignment in French sheep populations. BMC Genetics 18, 50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-017-0518-2 Viale E, Zanetti E, Özdemir D, Broccanello C, Dalmasso A, De Marchi M, Cassandro M (2017). Development and validation of a novel SNP panel for the genetic characterization of Italian chicken breeds by next-generation sequencing discovery and array genotyping. Poultry Science 96, 3858–3866. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pex238 Wehrenberg G, Tokarska M, Cocchiararo B, Nowak C (2024). A reduced SNP panel optimised for non-invasive genetic assessment of a genetically impoverished conservation icon, the European bison. Scientific Reports 14, 1875. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-51495-9
| Cost-efficient assignment panel for ducks. Setup of a cost-efficient assignment panel for duck populations. | Chapuis, Hervé, Brard-Fudulea, Sophie, Hazard, Azélie, Vignal, Alain, Demars, Julie, Rouger, Romuald, Teissier, Marc, Gilbert, Hélène | <p>The setup of a flexible and cost-effective 96-SNP assignment panel to be used in Pekin duck (<em>Anas platyrhynchos</em>), Muscovy duck (<em>Cairina moschata</em>) and their mule duck hybrid, is presented. SNP were selected on the available 600... |  | Animal genetics, Genomics | Seyed Abbas Rafat | 2024-04-12 09:45:59 | View | |
11 Dec 2023
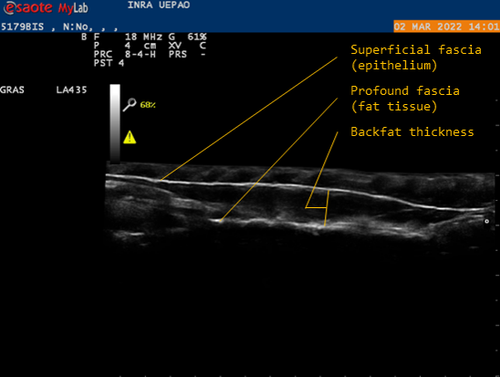
Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotypingNicolas Bédère, Joëlle Dupont, Yannick Baumard, Christophe Staub, David Gourichon, Frédéric Elleboudt, Pascale Le Roy, Tatiana Zerjal https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04172576Towards a better optimization of the genetic improvement of chicken breeds: Introduction of simple phenotypic traits related to body composition for easy measurement in the selection programs of laying hens.Recommended by Seyed Abbas Rafat based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In genetic selection, simplistic model of single-trait selection is usually considered, and the response to such approach is estimated using simple models. In practice, however, plant and animal breeders always deal with the selection of several traits, hence making the selection process very complex. Therefore, the simultaneous genetic improvement of several traits has always been one of the goals of livestock, including poultry breeding (Falconer, 1972). Studies that examine the indirect effects of selection on economic traits are eagerly awaited. In this context, the results of the study by Bédère et al., (2023) gives new insights about phenotypic and genotypic relationships between body reserves traits in laying hens. The authors aimed to propose novel data about the genetic architecture of traits related to body fat by measuring a series of phenotypic traits with relatively an easy approach. The authors further aimed to test and validate the phenotyping of backfat thickness as an indicator of the overall fatness of laying hens. Thus, the study allowed providing new evidence regarding the genetic determination of the backfat trait in chicken breeds. The authors first estimated the effect of selection on the residual feed intake (trait x) on the trait of body reserves (trait y). In fact, divergent selection experiments are a fundamental research tool that allow revealing significant amount of data related to the possible span of genetic improvement for traits of interest. Consequently, by analyzing data from a divergent selection experiment, associations have been estimated between a number of feed-dependent traits that have practical use for chicken breeders. Estimation of the correlations between traits is under question in terms of the theory of genetics and their application in multi-trait selection. As a major finding of the study, the observation of a bimodal distribution of backfat in both lines and the heterogeneity of the variances between families allowed suggesting a possible major gene, which could be investigated in future studies using for instance quantitative genetics. Body composition is continually studied in broilers chicken, but this aspect of chicken genetic is more detailed in laying hens. The current findings are worthy to validate using several approaches. In fact, one of the limitations of the study can be related to other statistical models that can be built. For example, the study revealed high correlations between egg production and body weight, thus body weight could be considered as a covariate in regression models. Moreover, the principal trait of selection (based on the residual feed intake) could be considered. References: Falconer, D. S. (1972). Introduction to Quantitative Genetics. Publisher: Ronald Press Company. pp 365. Bédère, N., Dupont, J., Baumard, Y., Staub, C., Gourichon, D., Elleboudt, F., Le Roy, P., Zerjal, T. (2023). Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotyping. HAL ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04172576 | Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotyping | Nicolas Bédère, Joëlle Dupont, Yannick Baumard, Christophe Staub, David Gourichon, Frédéric Elleboudt, Pascale Le Roy, Tatiana Zerjal | <p>In this study, we pursued three primary objectives: firstly to test and validate the phenotyping of backfat thickness as an indicator of the overall fatness of laying hens; secondly, to estimate genetic parameters for this trait; thirdly, to st... |  | Animal genetics, Poultry, Statistical genetics | Seyed Abbas Rafat | 2023-07-27 17:09:10 | View | |
27 Jul 2023
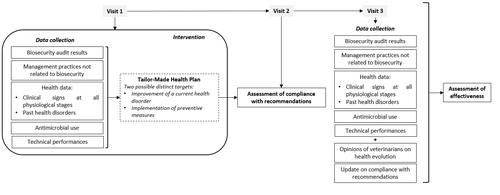
Combining several indicators to assess the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans in pig farmsLevallois Pierre, Leblanc-Maridor Mily, Scollo Annalisa, Ferrari Paolo, Belloc Catherine, Fourichon Christine https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7789634Evaluating tailor-made health plans in pig farms: a multiple complementary indicators approachRecommended by Matteo Chincarini based on reviews by Carla Gomes and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Carla Gomes and 1 anonymous reviewer
Tailor-made health plans for farming animals, including pigs, are highly beneficial due to their customized nature, addressing the unique needs of each farm and promoting efficient husbandry practices. However, assessing the effectiveness of individualized approaches can be challenging. Levallois et al. (1) tackled this challenge by evaluating the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans of pig farms based on a systematic biosecurity and herd health audit. The study involved twenty farrow-to-finish pig farms, each receiving specific plans tailored to their specific needs. Compliance with the recommendations was monitored over an eight-month period. In the literature, various studies have delved into specific issues in detail, such as disease incidence (e.g., (2)). However, the authors of this research applied a comprehensive approach through an integrative analysis of multiple complementary indicators to provide an effective evaluation of the changes and health disorders. The authors' holistic approach to measuring the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans is noteworthy. They employed up to seven methods to identify advantages and limitations, providing valuable insights for applied research and practitioners in the field of farm animals. Additionally, the study's inclusion of diverse farms, ranging from conventional to antibiotic-free and varying in sow breeding numbers (from 70 to 800), demonstrates the flexibility of the proposed approach, accommodating different farming systems. The study revealed three crucial considerations for future evaluations of tailor-made health plans. Firstly, placing compliance as the primary assessment indicator is a priority. Secondly, it is essential to tailor outcome indicators and monitoring periods according to each farm's specific health disorder. Lastly, a comprehensive understanding of the health disorder's evolution can be achieved through the amalgamation of multiple indicators. While the study does have limitations, such as the relatively short time window for assessment, the methodological framework and results are promising. Further, the discussion of the results raises several areas worthy of future investigation to improve compliance and address farmers' hesitations towards action (i.e., lack of willingness). More research in this context will be beneficial for veterinarians and practitioners, enhancing their understanding and positively impacting both farmers and animals. In conclusion, the study underscores the significant impact of tailor-made health plans on promoting positive changes in farm management. Assessing the effectiveness of these plans enables the refinement of new strategies and enhances the overall quality of work in animal production. The study by Levallois et al (1) sheds valuable light on the challenges and potentials of such plans, providing essential insights for pig farming practices. While further research and improvements are necessary, the study strongly emphasizes the pivotal role of individualized approaches in attaining improved farm management and enhancing animal welfare. 1. Levallois P, Leblanc-Maridor M, Scollo A, Ferrari P, Belloc C, Fourichon C. (2023). Combining several indicators to assess the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans in pig farms. Zenodo, 7789634. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7789634 2. Collineau L, Rojo-Gimeno C, Léger A, Backhans A, Loesken S, Nielsen EO, Postma M, Emanuelson U, grosse Beilage E, Sjölund M, Wauters E, Stärk KDC, Dewulf J, Belloc C, Krebs S. (2017). Herd-specific interventions to reduce antimicrobial usage in pig production without jeopardising technical and economic performance. Preventive veterinary medicine, 144:167-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2017.05.023 | Combining several indicators to assess the effectiveness of tailor-made health plans in pig farms | Levallois Pierre, Leblanc-Maridor Mily, Scollo Annalisa, Ferrari Paolo, Belloc Catherine, Fourichon Christine | <p style="text-align: justify;">A tailor-made health plan is a set of recommendations for a farmer to achieve and maintain a high health and welfare status. Tailored to each farm, it is intended to be an effective way of triggering change. This st... |  | Animal health, Veterinary science | Matteo Chincarini | 2023-03-31 19:02:35 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Karol B Barragán-Fonseca
Mohammed Gagaoua
Rachel Gervais
Florence Gondret
Francois Meurens
Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo*
Christian Nawroth
Seyed Abbas Rafat
Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas
* Representative









