Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * ▲ | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
23 Aug 2023
Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution?Birte L. Nielsen, Huw D.R. Golledge, Jen-Yun Chou, Irene Camerlink, Péter Pongrácz, Maria Camila Ceballos, Alexandra L. Whittaker and I. Anna S. Olsson https://www.doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/s6459Can a consensus be reached on the ethical review of animal experimentation for livestock species?Recommended by Hervé Acloque based on reviews by Christian Nawroth, Patrick Gonin and Leon borgdorf"Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution?" by Birte Nielsen and colleagues [1] provides food for thought on the ethical assessment of experiments involving farm animals. While regulations can provide a precise framework, they differ from country to country and do not consider several cases, mainly when the experimentation involves non- or minimally invasive manipulations. It is also the case when research projects use farmed animals that do not fall within the scope of the regulations on animal experimentation but have undergone practices that can be authorised on farms but may raise ethical questions (tail docking, live castration, tooth filing, beak trimming, dehorning). On the other hand, the heterogeneity of the criteria taken into account by the ethics committees, when they exist (and this can differ greatly from one country to another), do not necessarily correspond to the criteria of the journals, the reviewers and the bodies brought in to evaluate the research project, or to the regulations specific to each country. All these paradoxes lead the authors to propose solutions, the most straightforward and spontaneous of which is to ask ourselves questions about this issue upstream of the experimental design required to answer a given scientific question. While increasing the number of ethical review committees may be an insufficient option, the authors insist on the importance of improving committee members' training, taking into consideration jurisdictions' differences between countries and spending more time on ethics evaluation during manuscripts' reviewing. In addition, the upstream assessment of research projects by ethics committees, specific to an institution (research institute, universities, companies), a scientific publisher or even a dedicated international ethical review board may also be a good option. The ethical evaluation of research projects is a question at the heart of our research activities, for which we do not have all the answers. As with scientific reviewing, we must take on the role of evaluator or be evaluated ourselves, using criteria and feelings that are not always consensual. The heterogeneity of evaluation systems within the scientific community, the lack of training for scientists in the fundamentals of ethical evaluation, and the different perceptions of the animal condition between countries and cultures can lead to a reciprocal lack of understanding between evaluator and evaluated, and sometimes a feeling of injustice, as some research may be easy to conduct in one country but difficult in another. Indeed, it is exciting to read the exchanges between the authors and the three reviewers who assessed this opinion paper to appreciate the diversity of points of view and see specific points of divergence. In addition to animal experimentation, the judgment handed down on 30 June 2023 by the French court penalising a pig farmer for the abusive use of an authorised breeding practice (tail docking) is a perfect illustration of the fact that the ethical assessment of practices and handling of farm animals now extends far beyond the scientific world and is becoming an increasingly important factor in the relationship between society and animal breeding. Failure to consider this evolution, whether in experimentation or animal husbandry, may have legal consequences and increase the lack of understanding between our practices and how society perceives them. The questions raised and the solutions proposed in the article by Nielsen et al. are central to our concerns, not only for the scientific community but also to meet the expectations of all stakeholders. Finally, although the authors do not directly address the question of genome editing and research using edited farm animals, this is and will be at the heart of future issues concerning the ethical evaluation of research projects. As with practices and manipulations, the intentionality of the modifications induced leads us to question and evaluate, in farmed species, their consequences on animal welfare and their relevance to society and the development of more sustainable and socially accepted animal husbandry. Reference [1] Nielsen, B. L., Golledge, H. D. R., Chou, J., Camerlink, I., Pongrácz, P., Ceballos, M., Whittaker, A. L., Olsson, I. S. (2023) Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution? OSF Preprints. Ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/s6459 | Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution? | Birte L. Nielsen, Huw D.R. Golledge, Jen-Yun Chou, Irene Camerlink, Péter Pongrácz, Maria Camila Ceballos, Alexandra L. Whittaker and I. Anna S. Olsson | <p>As the article is a short Opinion Paper, it has no abstract, but it aims to highlight the inherent challenges to ethics review of animal (welfare) science research, especially the differences between different countries and jurisdictions which ... |  | Animal behaviour , Animal welfare, Open science, Veterinary science | Hervé Acloque | 2023-05-05 13:27:22 | View | |
14 Dec 2022
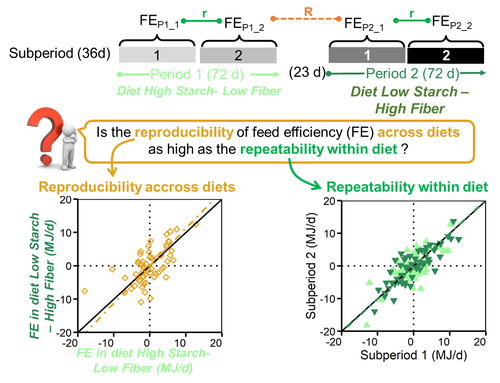
Feed efficiency of lactating Holstein cows was not as repeatable across diets as within diet over subsequent lactation stagesAmelie Fischer, Philippe Gasnier, philippe faverdin https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.10.430560A focus on feed efficiency reproducibility and repeatability of dairy cows fed different diets over the lactation stage.Recommended by Alberto Atzori based on reviews by Ioannis Kaimakamis, Angela Schwarm and 2 anonymous reviewersThe topic of feed efficiency is under discussion in the scientific community and several studies pointed out that lactation stage has to be accounted for when estimates of feed efficiency are carried out, especially for genetic ranking of animals and their performances, as highlighted by Li et al. (2017). Other researchers applied a latin square design to test dietary effects across lactation (Ipharraguerre et al. 2002) but this approach cannot be followed out of experimental conditions and particularly does not allow, nowadays, to valorize precision livestock farm data to get phenotypic information from individual animals at farm level. The current manuscript by Fischer, et al. (2022a) describes an experimental trial in which cows were first fed a high starch diet-low fibre then switched over to a low starch diet-high fibre and individually monitored over time. Data were analyzed with the objective to investigate effects within diets and across diets. Since all cows went through the same sequence at the same time it was not possible to completely separate the confounding effect of lactation stage and diet as stated by the authors. However, this manuscript adds methodological discussions and opens research questions especially to the matter of repeatability and reproducibility of feed efficiency of individual animals over the lactation stage. These variables are fundamental to evaluate nutritional traits and phenotypic performances of dairy cows at farm level, as highlighted by a paper of the same first author (Fischer, et al. 2022b) dealing to reproducibility and repeatability with a similar approach. My opinion is that this manuscript gives the opportunity to enlarge the scientific discussions on the calculation of repeatability and reproducibility of feed efficiency of individual animals over time. In particular, as in this study, specific mathematical approaches need to be carried out with the final goal to analyze and valorize precision livestock farm data for cow phenotyping and to propose new methods of feed efficiency evaluations. It also needs complete databases carried out under experimental conditions. In fact it has to be considered that this manuscript makes available to the scientific community all the data and the R code developed for data analysis giving the opportunity to replicate the calculations and propose new advancements in the feed efficiency evaluations of dairy cows. References Fischer A, Gasnier P, Faverdin P (2022a) Feed efficiency of lactating Holstein cows was not as repeatable across diets as within diet over subsequent lactation stages. bioRxiv, 2021.02.10.430560, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.10.430560 Fischer A, Dai X, Kalscheur KF (2022b) Feed efficiency of lactating Holstein cows is repeatable within diet but less reproducible when changing dietary starch and forage concentrations. animal, 16, 100599. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ANIMAL.2022.100599 Ipharraguerre IR, Ipharraguerre RR, Clark JH (2002) Performance of Lactating Dairy Cows Fed Varying Amounts of Soyhulls as a Replacement for Corn Grain. Journal of Dairy Science, 85, 2905–2912. https://doi.org/10.3168/JDS.S0022-0302(02)74378-6 Li B, Berglund B, Fikse WF, Lassen J, Lidauer MH, Mäntysaari P, Løvendahl P (2017) Neglect of lactation stage leads to naive assessment of residual feed intake in dairy cattle. Journal of Dairy Science, 100, 9076–9084. https://doi.org/10.3168/JDS.2017-12775
| Feed efficiency of lactating Holstein cows was not as repeatable across diets as within diet over subsequent lactation stages | Amelie Fischer, Philippe Gasnier, philippe faverdin | <p>Background: Improving feed efficiency has become a common target for dairy farmers to<br>meet the requirement of producing more milk with fewer resources. To improve feed<br>efficiency, a prerequisite is to ensure that the cows identified as mo... |  | Cattle production, Ruminant nutrition | Alberto Atzori | Anonymous, Ioannis Kaimakamis, Giuseppe Conte, Angela Schwarm | 2021-02-11 08:43:59 | View |
07 Oct 2024
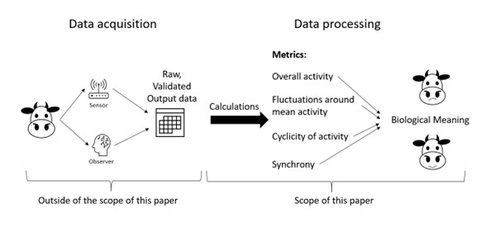
From data on gross activity to the characterization of animal behaviour: which metrics for which purposes?Ingrid D.E. van Dixhoorn, Lydiane Aubé, Coenraad van Zyl ,Rudi de Mol, Joop van der Werf, Romain Lardy, Marie Madeleine Mialon, Kees C.G. van Reenen, and Isabelle Veissier https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10420600A guide to improving the use of activity data in animal researchRecommended by Matteo Chincarini based on reviews by Birte L Nielsen and Anna Olsson based on reviews by Birte L Nielsen and Anna Olsson
In production animals, behavioural activity plays a crucial role across a wide range of scientific disciplines and is often measured for various purposes depending on the field: ethology, animal welfare, reproduction, animal production, and so on. Historically, direct observation was the primary method of collecting such data, a process that was time-consuming and prone to possible observer bias. With the advent of automated systems and sensors, behavioural activity can now be recorded continuously and non-invasively, leading to a growing body of more reliable data (1). However, the lack of standardisation in how these data are calculated and interpreted has created challenges for cross-study comparisons. To fully harness the potential of studying behavioural activity, scientific studies must harmonise the methods used to calculate this measure. Standardising these methods would make it easier to compare results and identify possible gaps in knowledge. In the work by van Dixhoorn et al.(2), the authors examine the various metrics most commonly used to study behavioural activity. Through a series of examples, they address the definitions, calculation methods, and biological significance of metrics such as overall activity, fluctuations around mean activity, cyclicity of activity, and synchrony between animals. The authors suggest how these different metrics can be applied in specific contexts and guide readers in using appropriate terminology to ensure future studies are more easily comparable. In addition, by clarifying these concepts, the authors provide researchers with the tools to make informed decisions about which metric best suits their study's objectives. A key contribution of this work is its emphasis on standardising the metrics and terminology used in behavioural activity studies. Studies using different metrics may arrive at conclusions that appear contradictory, not because of actual differences in animal behaviour, but due to inconsistencies in how behaviour is quantified. By advocating for a common framework, the authors aim to improve the replicability of studies, facilitate meta-analyses, and allow for a more cohesive understanding of animal behaviour across different research groups. This, in turn, could accelerate the identification of key behavioural indicators, ultimately leading to better animal management practices and welfare assessments. This article provides a timely and valuable contribution to the field of animal science. As technology continues to evolve, so too must our methods for interpreting the vast amounts of data it generates (3). By ensuring that studies are comparable and data is interpreted consistently, the research community can work towards more meaningful discoveries in animal behaviour. I highly recommend this paper to researchers looking to deepen their understanding of activity metrics in animal behaviour studies. References 1. Rushen J, Chapinal N, de Passilé AM (2012). Automated monitoring of behavioural-based animal welfare indicators. Animal Welfare 21(3):339-50. https://doi.org/10.7120/09627286.21.3.339 2. van Dixhoorn IDE, Aubé L, van Zyl C, de Mol R, van der Werf J, Lardy R, Mialon MM, van Reenen CG, and Veissier I (2024). From data on gross activity to the characterization of animal behaviour: which metrics for which purposes?. Zenodo, 10420600, ver.5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10420600 3. Riaboff L, Shalloo L, Smeaton AF, Couvreur S, Madouasse A, Keane MT (2022). Predicting livestock behaviour using accelerometers: A systematic review of processing techniques for ruminant behaviour prediction from raw accelerometer data. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 192:106610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.106610 | From data on gross activity to the characterization of animal behaviour: which metrics for which purposes? | Ingrid D.E. van Dixhoorn, Lydiane Aubé, Coenraad van Zyl ,Rudi de Mol, Joop van der Werf, Romain Lardy, Marie Madeleine Mialon, Kees C.G. van Reenen, and Isabelle Veissier | <p>The behaviour of an animal is closely linked to its internal state. Various metrics can be calculated from activity data. Complex patterns of activity within or between individuals, such as cyclic patterns and synchrony, can inform on the biolo... |  | Animal behaviour , Animal health, Animal welfare, Precision livestock farming | Matteo Chincarini | 2023-12-21 23:36:35 | View | |
11 Dec 2023
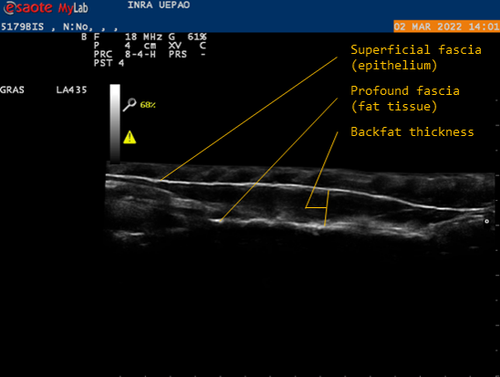
Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotypingNicolas Bédère, Joëlle Dupont, Yannick Baumard, Christophe Staub, David Gourichon, Frédéric Elleboudt, Pascale Le Roy, Tatiana Zerjal https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04172576Towards a better optimization of the genetic improvement of chicken breeds: Introduction of simple phenotypic traits related to body composition for easy measurement in the selection programs of laying hens.Recommended by Seyed Abbas Rafat based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In genetic selection, simplistic model of single-trait selection is usually considered, and the response to such approach is estimated using simple models. In practice, however, plant and animal breeders always deal with the selection of several traits, hence making the selection process very complex. Therefore, the simultaneous genetic improvement of several traits has always been one of the goals of livestock, including poultry breeding (Falconer, 1972). Studies that examine the indirect effects of selection on economic traits are eagerly awaited. In this context, the results of the study by Bédère et al., (2023) gives new insights about phenotypic and genotypic relationships between body reserves traits in laying hens. The authors aimed to propose novel data about the genetic architecture of traits related to body fat by measuring a series of phenotypic traits with relatively an easy approach. The authors further aimed to test and validate the phenotyping of backfat thickness as an indicator of the overall fatness of laying hens. Thus, the study allowed providing new evidence regarding the genetic determination of the backfat trait in chicken breeds. The authors first estimated the effect of selection on the residual feed intake (trait x) on the trait of body reserves (trait y). In fact, divergent selection experiments are a fundamental research tool that allow revealing significant amount of data related to the possible span of genetic improvement for traits of interest. Consequently, by analyzing data from a divergent selection experiment, associations have been estimated between a number of feed-dependent traits that have practical use for chicken breeders. Estimation of the correlations between traits is under question in terms of the theory of genetics and their application in multi-trait selection. As a major finding of the study, the observation of a bimodal distribution of backfat in both lines and the heterogeneity of the variances between families allowed suggesting a possible major gene, which could be investigated in future studies using for instance quantitative genetics. Body composition is continually studied in broilers chicken, but this aspect of chicken genetic is more detailed in laying hens. The current findings are worthy to validate using several approaches. In fact, one of the limitations of the study can be related to other statistical models that can be built. For example, the study revealed high correlations between egg production and body weight, thus body weight could be considered as a covariate in regression models. Moreover, the principal trait of selection (based on the residual feed intake) could be considered. References: Falconer, D. S. (1972). Introduction to Quantitative Genetics. Publisher: Ronald Press Company. pp 365. Bédère, N., Dupont, J., Baumard, Y., Staub, C., Gourichon, D., Elleboudt, F., Le Roy, P., Zerjal, T. (2023). Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotyping. HAL ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-04172576 | Genetic background of body reserves in laying hens through backfat thickness phenotyping | Nicolas Bédère, Joëlle Dupont, Yannick Baumard, Christophe Staub, David Gourichon, Frédéric Elleboudt, Pascale Le Roy, Tatiana Zerjal | <p>In this study, we pursued three primary objectives: firstly to test and validate the phenotyping of backfat thickness as an indicator of the overall fatness of laying hens; secondly, to estimate genetic parameters for this trait; thirdly, to st... |  | Animal genetics, Poultry, Statistical genetics | Seyed Abbas Rafat | 2023-07-27 17:09:10 | View | |
20 Aug 2024

Goats who stare at video screens – assessing behavioural responses of goats towards images of familiar and unfamiliar con- and heterospecificsJana Deutsch, Steve Lebing, Anja Eggert, Christian Nawroth https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/d4nzkGazing behaviour as a tool to study goat cognitionRecommended by Isabelle Veissier based on reviews by Richard Bon and 1 anonymous reviewerMany cognitive studies use paradigms based on active decision-making, that require that animals are motivated to participate and interested in the reward (e.g. Rivas-Blanco et al., 2023). By contrast, looking time paradigms, in which the visual attention of an animal to a stimulus is measured, requires little training and little action from the subject, and can be used without reinforcement (e.g. Wilson et al., 2023). In this methodological paper, Jana Deutsch and her collaborators investigated the possibility of using a looking time paradigm to study perception and cognition in goats. The advantage of such a paradigm would be that it requires little training and can be used with no reinforcement. Goats were observed in front of two video screens presenting pictures of goats (familiar or not), of humans (familiar or not), or remaining white. The authors hypothesised that goats would pay more attention to pictures than to a white screen, would pay more attention to goats than to humans, and would discriminate familiar vs. unfamiliar beings. The goats had received previous positive contacts with the familiar humans. The goats were extensively habituated to the experimental set-up so that stress did not interfere in responses to testing. The stimuli were presented on the screens in a pseudorandomized and counterbalanced order. As hypothesised, goats looked longer at screen with pictures, and longer when the picture was that of another goat (familiar or not) than of a human being. Goats however did not seem to discriminate between familiar and unfamiliar being, or were equally motivated by the two types of beings. Ear postures were also recorded but did not show a relation with looking time and were not related to the type of picture shown on screens. Therefore, the authors argue that looking time but not ear posture is considered appropriate to test discrimination abilities or preferences in goats. More studies are needed to check if goats can differentiate familiar vs. unfamiliar beings. The experimental design is sound. The statistical analyses are rigorous and very relevant. The paper is clearly written. I recommend the manuscript for publication for its originality and its quality; In addition, the paper bring findings – that looking time is an adequate paradigm in goats to analyse how they pay attention to stimuli – that have potential impacts on further studies in animal cognition. References Deutsch, J., Lebing, S., Eggert, A., Nawroth, C. (2024). Goats who stare at video screens – assessing behavioural responses of goats towards images of familiar and unfamiliar con- and heterospecifics. OSF, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/d4nzk Rivas-Blanco, D., Monteiro, T., Virányi, Z., Range, F. (2024). Going back to “basics”: Harlow’s learning set task with wolves and dogs. Learning & Behavior. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13420-024-00631-6 Wilson, V. A. D., Bethell, E. J., Nawroth, C. (2023). The use of gaze to study cognition: limitations, solutions, and applications to animal welfare. Frontiers in Psychology, 14:1147278. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1147278
| Goats who stare at video screens – assessing behavioural responses of goats towards images of familiar and unfamiliar con- and heterospecifics | Jana Deutsch, Steve Lebing, Anja Eggert, Christian Nawroth | <p>Many cognitive paradigms rely on active decision-making, creating participation biases (e.g. subjects may lack motivation to participate in the training) and once-learned contingencies may bias the outcomes of subsequent similar tests. We here ... |  | Animal behaviour , Animal cognition, Animal welfare, Small ruminants | Isabelle Veissier | 2023-12-05 13:07:18 | View | |
24 May 2022
Identifying cattle with superior growth feed efficiency through their natural 15N abundance and plasma urea concentration: a meta-analysis.Gonzalo Cantalapiedra-Hijar, Isabelle Morel, Bernard Sepchat, Céline Chantelauze, Gemma A. Miller, Carol-Anne Duthie, Isabelle Ortigues-Marty, Richard J. Dewhurst https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.578396015N as a marker for feed efficiency in beef cattleRecommended by Marcos Marcondes based on reviews by Emilio Mauricio Ungerfeld and 1 anonymous reviewerIdentifying individuals with a more remarkable feed efficiency may positively affect the profitability and sustainability of the beef industry (Cruz et al., 2010; Basarab et al., 2013). However, although most international nutrient requirements systems predict animal feed efficiency, intake data is usually unavailable at the farm level, and ranking animals based on efficiency might be challenging. In this sense, using differences in the occurrence of isotopic N between animal and diet (Δ15Nanimal-diet) might become a natural biomarker to determine feed efficiency at the farm level. This methodology was firstly demonstrated by Guarnido-Lopez et al. (2021). In the present study by Cantalapiedra-Hijar et al. (2022), the authors evaluated the extent to which Δ15Nanimal-diet can be used as a marker for feed efficiency in beef animals. For this, a meta-analysis was conducted using a database including 759 individual records for performance and N isotopic discrimination measured in plasma or muscle (Δ15Nanimal-diet; n = 749) and plasma urea concentration (n = 659). The database was composed of 37% Charolais, 15% Simmental, and 40% of beef crossbreds. The results confirmed that Δ15Nanimal-diet could discriminate animals with at least 0.10 kg/kg difference in feed efficiency. Furthermore, the Δ15Nanimal-diet marker also successfully discriminated the feed efficiency of two animals from the same contemporary group if they differ by at least 0.06 kg/kg of FCE. However, when trying to predict feed efficiency, using the two candidate biomarkers did not improve estimates. Lastly, when data from biomarkers were combined with performance data, improvement in the predictions was observed. Nonetheless, the present results warrant more studies to evaluate the use of Δ15Nanimal-diet as a biomarker for feed efficiency since it could be used not only for feed efficiency discrimination but also in genetic selections.
References Cantalapiedra-Hijar G, Morel I, Sepchat B, Chantelauze C, Miller GA, Duthie CA, Ortigues-Marty I, Dewhurst RJ (2022). Identifying cattle with superior growth feed efficiency through their natural 15N abundance and plasma urea concentration: A meta-analysis. Zenodo, 5783960, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5783960. Cruz GD, Rodríguez-Sánchez JA, Oltjen JW, Sainz RD (2010). Performance, residual feed intake, digestibility, carcass traits, and profitability of Angus-Hereford steers housed in individual or group pens. J. Anim. Sci. 88:324-329. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2009-1932. Basarab JA, Beauchemin KA, Baron VS, Ominski KH, Guan LL, Miller SP, Crowley JJ (2013). Reducing GHG emissions through genetic improvement for feed efficiency: effects on economically important traits and enteric methane production. Animal 7:303-315. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731113000888. Guarnido-Lopez P, Ortigues-Marty I, Taussat S, Fossaert C, Renand G, Cantalapiedra-Hijar G (2021). Plasma proteins Δ15N vs. plasma urea as candidate biomarkers of between-animal variations of feed efficiency in beef cattle: Phenotypic and genetic evaluation. Animal 15:100318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.animal.2021.100318.
| Identifying cattle with superior growth feed efficiency through their natural 15N abundance and plasma urea concentration: a meta-analysis. | Gonzalo Cantalapiedra-Hijar, Isabelle Morel, Bernard Sepchat, Céline Chantelauze, Gemma A. Miller, Carol-Anne Duthie, Isabelle Ortigues-Marty, Richard J. Dewhurst | <p>The objective of this study was to test two candidate biomarkers of feed efficiency in growing cattle. A database was built using performance data from 13 trials conducted with growing heifers, steers and young bulls and testing 34 dietary trea... | Physiology, Ruminant nutrition | Marcos Marcondes | 2021-12-07 15:24:15 | View | ||
05 Jul 2022
Impact of pre-breeding feeding practices on rabbit mammary gland development at mid-pregnancy.Cathy Hue-Beauvais, Karine Bebin, Raphael Robert, Delphine Gardan-Salmon, Mickael Maupin, Nicolas Brun, Etienne Aujean, Florence Jaffrezic, Steve Simon, Madia Charlier, Fabienne Le Provost https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.17.476562Managing the feeding of rabbits to improve metabolic efficiencyRecommended by Giuseppe Conte based on reviews by Marion Boutinaud, Davi Savietto and 1 anonymous reviewerA correct execution of feeding plan for growing rabbit decreases the possibility of post-weaning digestive disorders, thus enhancing the feed efficiency in the animals. However, a limitation of feed daily quantity is required between 10 weeks of age and the first artificial insemination. This limitation causes energy deficiency with a consequent reduction in fertility. Beauvais et al. (2022) studied the impact of feed restriction strategies in female rabbits. Four feed restriction strategies were applied in two distinct periods (post-weaning and puberty) and evaluated by different physiological parameters (growth rate, metabolic profiles, reproductive parameters and mammary gland development). In the first part of the paper, the authors evaluated the association between weight slopes and feeding strategies in the late post-weaning and peripartum period in the four groups. As revealed by the authors, a significant difference was observed during the late post-weaning period, which remained significant between the pubertal and fattening phases. Probably these differences are related to the restriction feeding pattern. The results indicated that restrictive feeding changes in the first step of post-weaning period is associated with a significant difference in body weight. This difference occurs from the third week of diet, highlighting the high sensitivity of growing rabbit to nutrition during the post-weaning period. In the second part of the paper, the authors evaluated the expression of genes involved in the lipid metabolism. During the mid-pregnancy, was revealed a significant higher expression of lipogenic genes, which may be considered as useful markers for the mammary epithelial development in less restrictive strategies during early life period. The results proposed by Beauvais et al. (2022) enlighten the important role played by the feeding conditions of young female rabbits in the early life rearing. In particular, this activity provides specific recommendations for optimizing lactation and thus preventing neonatal mortality of the offspring. Moreover, the authors provide indications about the effect of feeding strategies on the mammary development and gene expression with absolute consequences on the development of offspring. Mammary lipid metabolism affects the milk profile and therefore the growth performance of the young animals. Reference
Hue-Beauvais C, Bebin K, Robert R, Gardan-Salmon D, Maupin M, Brun N, Aujean E, Jaffrezic F, Simon S, Charlier M, Le Provost F (2022). Impact of pre-breeding feeding practices on rabbit mammary gland development at mid-pregnancy. biorXiv, 2022.01.17.476562, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.17.476562 | Impact of pre-breeding feeding practices on rabbit mammary gland development at mid-pregnancy. | Cathy Hue-Beauvais, Karine Bebin, Raphael Robert, Delphine Gardan-Salmon, Mickael Maupin, Nicolas Brun, Etienne Aujean, Florence Jaffrezic, Steve Simon, Madia Charlier, Fabienne Le Provost | <p>Optimizing rabbit does preparation during early life to improve reproductive potential is a major challenge for breeders. Does selected for reproduction have specific nutritional needs, which may not be supplied with the common practice of feed... |  | Animal nutrition modelling | Giuseppe Conte | 2022-01-19 14:44:30 | View | |
06 Sep 2019
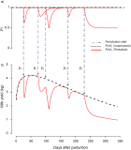
Lactation curve model with explicit representation of perturbations as a phenotyping tool for dairy livestock precision farming.Ben Abdelkrim Ahmed, Puillet Laurence, Gomes Pierre, Martin Olivier https://doi.org/10.1101/661249Developing smart fitting algorithms to identify random perturbations in time-series dataRecommended by Luis Tedeschi based on reviews by Alberto Atzori, Jennifer Spencer and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Alberto Atzori, Jennifer Spencer and 1 anonymous reviewer
The ability to adequately characterize the lactation curve of livestock is important not only to ensure proper nutrition of the lactating animal but, among many other benefits, it can assist in diagnosing the incidence of diseases, predicting the quantity of milk production, and comparing animals within the herd for managerial strategies such as culling. Eventually, such smart fitting algorithms can lead to improved genetic selection of more productive animals after genetic-unrelated noises are removed from the data, systematically. References [1] Johansson, I. (1961). Genetic Aspects of Dairy Cattle Breeding. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, IL. [2] Nelder, J. A. (1966). Inverse polynomials, a useful group of multi-factor response functions. Biometrics. 22 (1):128-141. doi: 10.2307/2528220 | Lactation curve model with explicit representation of perturbations as a phenotyping tool for dairy livestock precision farming. | Ben Abdelkrim Ahmed, Puillet Laurence, Gomes Pierre, Martin Olivier | <p>Background Understanding the effects of environment on livestock provides valuable information on how farm animals express their production potential, and on their welfare. Ruminants are often confronted with perturbations that affect their per... |  | Lactation biology , Mathematical modelling, Precision livestock farming | Luis Tedeschi | 2019-06-07 09:38:26 | View | |
28 Jan 2022
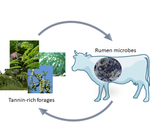
Microbial colonization of tannin-rich tropical plants: interplay between degradability, methane production and tannin disappearance in the rumenMoufida Rira, Diego P Morgavi, Milka Popova, Gaelle Maxin, Michel Doreau https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.12.456105Ruminal microbial degradation of tannin-rich tropical plants and methane productionRecommended by Antonio Faciola based on reviews by Todd Callaway and Srinivasan MahalingamRira et al. (2022) evaluated ruminal degradation of tropical tannins-rich plants and the relationship between condensed tannins disappearance and microbial communities. I found this study relevant because a major limitation for tropical plants utilization by ruminants is their potential reduced nutrient digestion. In this study, authors used leaves from Calliandra calothyrsus, Gliricidia sepium, and Leucaena leucocephala, pods from Acacia nilotica and the leaves of Manihot esculenta and Musa spp., which were incubated in situ in the rumen of dairy cows. An in vitro approach was also used to assess the effects of these plants on ruminal fermentation. They observed that hydrolysable and free condensed tannins from all plants completely disappeared after 24 h incubation in the rumen. Disappearance of protein-bound condensed tannins was variable with values ranging from 93% for Gliricidia sepium to 21% for Acacia nilolitica. This demonstrated some potential for selection and improvements in protein digestion. In contrast, fibre-bound condensed tannins disappearance averaged ~82% and did not vary between plants, which was remarkable. The authors noted that disappearance of bound fractions of condensed tannins was not associated with degradability of plant fractions and that the presence of tannins interfered with the microbial colonisation of plants. Each plant had distinct bacterial and archaeal communities after 3 and 12 h of incubation in the rumen and distinct protozoal communities at 3 h. This suggests a great deal of specificity for microbial-plant interactions, which warrants further evaluation to consider also animal contributions to such specificity. Adherent communities in tannin-rich plants had a lower relative abundance of fibrolytic microbes, notably Fibrobacter spp. Whereas, archaea diversity was reduced in high tannin-containing Calliandra calothyrsus and Acacia nilotica at 12 h of incubation. Concurrently, in vitro methane production was lower for Calliandra calothyrsus, Acacia nilotica and Leucaena leucocephala although for the latter total volatile fatty acids production was not affected and was similar to control. Finally, the study demonstrated that the total amount of hydrolysable and condensed tannins contained in a plant play a role governing the interaction with rumen microbes affecting degradability and fermentation. The effect of protein- and fibre-bound condensed tannins on degradability is less important. The major limitation of the study is the lack of animal validation at this stage; therefore, further studies are warranted, especially studies evaluating these plants in vivo. Furthermore, mechanisms associated with plant-microbial specificity, the role played by the host, and more data on nutrient utilization and gas production should be investigated. Nonetheless, this work show interesting microbial colonization and specific plant-microbial relationships that are novel in the ruminal environment. Reference: Rira M, Morgavi DP, Popova M, Maxin G, Doreau M (2022). Microbial colonization of tannin-rich tropical plants: interplay between degradability, methane production and tannin disappearance in the rumen. bioRxiv, 2021.08.12.456105, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.12.456105
| Microbial colonization of tannin-rich tropical plants: interplay between degradability, methane production and tannin disappearance in the rumen | Moufida Rira, Diego P Morgavi, Milka Popova, Gaelle Maxin, Michel Doreau | <p>Condensed tannins in plants are found free and attached to protein and fibre but it is not<br>known whether these fractions influence rumen degradation and microbial colonization.<br>This study explored the rumen degradation of tropical tannins... |  | Animal nutrition modelling, Cattle production, Emissions , Farming systems, Gut microbiology, Microbial ecology, Microbial fermentation, Rumen microbiology, Rumen microbiome , Ruminant nutrition | Antonio Faciola | 2021-08-16 08:56:45 | View | |
16 Apr 2021
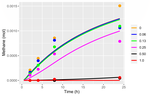
Modelling the impact of the macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis on rumen microbial fermentation and methane productionRafael Muñoz-Tamayo , Juana C. Chagas, Mohammad Ramin, Sophie J. Krizsan https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.09.374330Understanding the mechanisms behind natural bioactive compounds that can potentially reduce methane production in anaerobic conditions. A case study of Asparagopsis taxiformisRecommended by Luis Tedeschi based on reviews by Alberto Atzori, Henk van Lingen and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Alberto Atzori, Henk van Lingen and 2 anonymous reviewers
Naturally occurring compounds that can reduce methane production in anaerobic conditions have been studied for quite some time as feasible approaches to mitigate methane production in ruminant animals, especially those of commercial importance. Asparagopsis taxiformis (red algae) and Dictyota bartayresii (brown algae) are effective inhibitors of methane synthesis under in vitro anaerobic fermentation systems (Machado et al., 2014) likely because of their high concentration of secondary metabolites that are toxic to the typical rumen microbiota, including protozoa. In addition to phytoplankton (Palmer and Reason, 2009), Asparagopsis contains a high concentration of haloform compounds (e.g., bromoform, chloroform) while Dictyota has a high concentration of isoprenoid terpenes. Despite the economic and biological impact of diverse phytochemicals on reducing methane production in ruminant animals (Tedeschi et al., 2021), haloform compounds’ environmental impact and safety, in particular, are still unclear. In the present study, Munõz-Tamayo and collaborators (2021) listed relevant literature about the impact of A. taxiformis on ruminal methane production. Concurrent to the understanding of mechanisms and biology behind the reduction of ruminal methane, mathematical models can lead the way to enhance the effectiveness of feeding A. taxiformis under commercial applications. Thus, in the present study, Munõz-Tamayo and collaborators (2021) sought to develop a mathematical model to understand the rumen fermentation changes in vitro experimentation containing extract of A. taxiformis by adapting a previously documented model by Muñoz-Tamayo et al. (2016). Modeling development, calibration, and evaluation steps should be independent of each other, requiring complete, distinct, and separate databases (Tedeschi, 2006). However, in rare circumstances where such requirements cannot be met because data availability is scarce, the cross-validation technique, when possible, should be considered to assess data dispersion’s effects on model adequacy. In other situations, clear reasoning for failing to do so must be addressed in the paper. In the present paper, Munõz-Tamayo and collaborators (2021) explained the limitations in their modeling efforts were primarily due to the lack of ideal data: “experiments with simultaneous dynamic data of bromoform, volatile fatty acids, hydrogen, and methane.” Regardless of the availability of ideal data, improvements in the conceptual model are warranted to include amino acids and branched-chain fatty acids fermentation dynamics in the rumen and the fluctuations in ruminal pH. References Machado L, Magnusson M, Paul NA, Nys R de, Tomkins N (2014) Effects of Marine and Freshwater Macroalgae on In Vitro Total Gas and Methane Production. PLOS ONE, 9, e85289. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085289 Muñoz-Tamayo R, Chagas JC, Ramin M, Krizsan SJ (2021) Modelling the impact of the macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis on rumen microbial fermentation and methane production. bioRxiv, 2020.11.09.374330, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.09.374330 Muñoz-Tamayo R, Giger-Reverdin S, Sauvant D (2016) Mechanistic modelling of in vitro fermentation and methane production by rumen microbiota. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 220, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.07.005 Palmer CJ, Reason CJ (2009) Relationships of surface bromoform concentrations with mixed layer depth and salinity in the tropical oceans. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 23. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GB003338 Tedeschi LO (2006) Assessment of the adequacy of mathematical models. Agricultural Systems, 89, 225–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2005.11.004 Tedeschi LO, Muir JP, Naumann HD, Norris AB, Ramírez-Restrepo CA, Mertens-Talcott SU (2021) Nutritional Aspects of Ecologically Relevant Phytochemicals in Ruminant Production. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.628445 | Modelling the impact of the macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis on rumen microbial fermentation and methane production | Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo , Juana C. Chagas, Mohammad Ramin, Sophie J. Krizsan | <p>Background: The red macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis is a potent natural supplement for reducing methane production from cattle. A. taxiformis contains several anti-methanogenic compounds including bromoform that inhibits directly methanogene... |  | Agricultural sustainability, Animal nutrition modelling, Emissions , Mathematical modelling, Microbial fermentation, Rumen microbiology, Rumen microbiome | Luis Tedeschi | 2020-11-17 06:28:29 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Karol B Barragán-Fonseca
Mohammed Gagaoua
Rachel Gervais
Florence Gondret
Francois Meurens
Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo*
Christian Nawroth
Seyed Abbas Rafat
Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas
* Representative









