Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * ▲ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
31 Jan 2020

OneARK: Strengthening the links between animal production science and animal ecologyDelphine Destoumieux-Garzón, Pascal Bonnet, Céline Teplitsky, François Criscuolo, Pierre-Yves Henry, David Mazurais, Patrick Prunet, Gilles Salvat, Philippe Usseglio-Polatera, Etienne Verrier and Nicolas Friggens https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3632731When scientific communities intertwineRecommended by Pauline Ezanno based on reviews by Rowland Raymond Kao, Arata Hidano and 1 anonymous reviewerScientific research can be seen by some as a competitive territory: competition of opinions, concepts, publications, competition for funding. Fortunately, it is above all a territory of sharing and cross-fertilization of ideas. It is gradually becoming a territory of productive interdisciplinary collaborations, despite persistent resistance to making borders more permeable [1]. At the crossroads of worlds, many challenges must be met for communities to understand each other, to be able to communicate with one another, and to benefit mutually from scientific interactions [2]. Delphine Destoumieux-Garzon and co-authors [3] propose to stimulate a single Animal Research Kinship (OneARK) to promote the crossing of the scientific communities in animal production and animal ecology. These two communities share many concepts and methods, which, while they are based on marked specificities (natural versus artificial systems), also and above all have common points that need to be explored more closely. Seven concepts of shared interest to improve the resilience and sustainability of animal population systems were explored by the authors: selection, system viability, system management, animal adaptability, inter-individual diversity in systems, agroecology, and animal monitoring. This foundation stone paves the way for a finer integration between these two communities, which are close and yet distant, and which are slowly getting to know, understand, and recognize each other. References [1] Ledford, H. (2015). How to solve the world’s biggest problems. Nature, 525, 308–311. doi: 10.1038/525308a | OneARK: Strengthening the links between animal production science and animal ecology | Delphine Destoumieux-Garzón, Pascal Bonnet, Céline Teplitsky, François Criscuolo, Pierre-Yves Henry, David Mazurais, Patrick Prunet, Gilles Salvat, Philippe Usseglio-Polatera, Etienne Verrier and Nicolas Friggens | <p>1. Wild and farmed animals are key elements of natural and managed ecosystems that deliver functions such as pollination, pest control and nutrient cycling within the broader roles they play in contributing to biodiversity and to every category... |  | Agricultural sustainability, Animal genetics, Animal welfare, Ecology, Precision livestock farming, Veterinary epidemiology | Pauline Ezanno | 2019-07-05 15:33:21 | View | |
16 Apr 2021
Modelling the impact of the macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis on rumen microbial fermentation and methane productionRafael Muñoz-Tamayo , Juana C. Chagas, Mohammad Ramin, Sophie J. Krizsan https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.09.374330Understanding the mechanisms behind natural bioactive compounds that can potentially reduce methane production in anaerobic conditions. A case study of Asparagopsis taxiformisRecommended by Luis Tedeschi based on reviews by Alberto Atzori, Henk van Lingen and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Alberto Atzori, Henk van Lingen and 2 anonymous reviewers
Naturally occurring compounds that can reduce methane production in anaerobic conditions have been studied for quite some time as feasible approaches to mitigate methane production in ruminant animals, especially those of commercial importance. Asparagopsis taxiformis (red algae) and Dictyota bartayresii (brown algae) are effective inhibitors of methane synthesis under in vitro anaerobic fermentation systems (Machado et al., 2014) likely because of their high concentration of secondary metabolites that are toxic to the typical rumen microbiota, including protozoa. In addition to phytoplankton (Palmer and Reason, 2009), Asparagopsis contains a high concentration of haloform compounds (e.g., bromoform, chloroform) while Dictyota has a high concentration of isoprenoid terpenes. Despite the economic and biological impact of diverse phytochemicals on reducing methane production in ruminant animals (Tedeschi et al., 2021), haloform compounds’ environmental impact and safety, in particular, are still unclear. In the present study, Munõz-Tamayo and collaborators (2021) listed relevant literature about the impact of A. taxiformis on ruminal methane production. Concurrent to the understanding of mechanisms and biology behind the reduction of ruminal methane, mathematical models can lead the way to enhance the effectiveness of feeding A. taxiformis under commercial applications. Thus, in the present study, Munõz-Tamayo and collaborators (2021) sought to develop a mathematical model to understand the rumen fermentation changes in vitro experimentation containing extract of A. taxiformis by adapting a previously documented model by Muñoz-Tamayo et al. (2016). Modeling development, calibration, and evaluation steps should be independent of each other, requiring complete, distinct, and separate databases (Tedeschi, 2006). However, in rare circumstances where such requirements cannot be met because data availability is scarce, the cross-validation technique, when possible, should be considered to assess data dispersion’s effects on model adequacy. In other situations, clear reasoning for failing to do so must be addressed in the paper. In the present paper, Munõz-Tamayo and collaborators (2021) explained the limitations in their modeling efforts were primarily due to the lack of ideal data: “experiments with simultaneous dynamic data of bromoform, volatile fatty acids, hydrogen, and methane.” Regardless of the availability of ideal data, improvements in the conceptual model are warranted to include amino acids and branched-chain fatty acids fermentation dynamics in the rumen and the fluctuations in ruminal pH. References Machado L, Magnusson M, Paul NA, Nys R de, Tomkins N (2014) Effects of Marine and Freshwater Macroalgae on In Vitro Total Gas and Methane Production. PLOS ONE, 9, e85289. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085289 Muñoz-Tamayo R, Chagas JC, Ramin M, Krizsan SJ (2021) Modelling the impact of the macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis on rumen microbial fermentation and methane production. bioRxiv, 2020.11.09.374330, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.09.374330 Muñoz-Tamayo R, Giger-Reverdin S, Sauvant D (2016) Mechanistic modelling of in vitro fermentation and methane production by rumen microbiota. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 220, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.07.005 Palmer CJ, Reason CJ (2009) Relationships of surface bromoform concentrations with mixed layer depth and salinity in the tropical oceans. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 23. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GB003338 Tedeschi LO (2006) Assessment of the adequacy of mathematical models. Agricultural Systems, 89, 225–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2005.11.004 Tedeschi LO, Muir JP, Naumann HD, Norris AB, Ramírez-Restrepo CA, Mertens-Talcott SU (2021) Nutritional Aspects of Ecologically Relevant Phytochemicals in Ruminant Production. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.628445 | Modelling the impact of the macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis on rumen microbial fermentation and methane production | Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo , Juana C. Chagas, Mohammad Ramin, Sophie J. Krizsan | <p>Background: The red macroalgae Asparagopsis taxiformis is a potent natural supplement for reducing methane production from cattle. A. taxiformis contains several anti-methanogenic compounds including bromoform that inhibits directly methanogene... |  | Agricultural sustainability, Animal nutrition modelling, Emissions , Mathematical modelling, Microbial fermentation, Rumen microbiology, Rumen microbiome | Luis Tedeschi | 2020-11-17 06:28:29 | View | |
15 Dec 2020
Accuracy of predicting chemical body composition of growing pigs using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometryClaudia Kasper, Patrick Schlegel, Isabel Ruiz-Ascacibar, Peter Stoll, Giuseppe Bee https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.15.286153Accurate predictions of chemical composition of pigs for a wide range of body weights: no longer a myth!Recommended by Florence Gondret based on reviews by Mathieu Monziols and 1 anonymous reviewerAssessing body or carcass composition in growing pigs is essential to refine nutritional models, select for specific traits and evaluate pork products. The gold standard methods are dissection and chemical measurements, which are time-consuming and invasive ways to obtain the data. Different teams have tested dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), especially for determining total and regional body composition of fat, soft lean tissues and bone minerals [1-3]. The DEXA measurements are quick, non-invasive, precise, and operator independent. However, the instruments from different manufacturers are unique in implementation so that it is difficult to obtain and share generalized equations. In addition, the validity and accuracy of the measures when applied to pigs having very different composition have been scarcely addressed.
The present manuscript shows that carcass analysis by DEXA can be used to predict empty body chemical composition, and it provides accuracy values for the content in single nutrients (protein, lipids, Ca, P). The body weight range used to generate differences in body composition is very large (20 to 100 kg), which is important when studying pigs along growth. Moreover, regression equations within weight classes (20, 60 and 100 kg) show no important biases, with the exception for body fat especially at the earliest growth stages. Limitations of the technique are the needs of anesthesia when applied to living pigs, and of standardizing the positions of body, carcass and cuts when applied to living or dissected pigs. Another originality of the manuscript is the comparison of the obtained calibrations with previously published prediction models, showing that the differences do not preclude the possibility to use a single model when built from a meta-analysis of the different data. Taken together, this work offers good perspectives to refine nutritional models by inputs from rapidly analyzed body chemical composition and to monitor body and carcass composition in several pigs for genetics applications.
References [1] Mitchell AD., Scholz AM., Pursel VG., and Evock-Clover CM. (1998). Composition analysis of pork carcasses by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Journal of Animal Science. 76(8), 2104-14. https://doi.org/10.2527/1998.7682104x [2] Marcoux M., Bernier JF., and Pomar C. (2003). Estimation of Canadian and European lean yields and composition of pig carcasses by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Meat Science. 63(3), 359-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1740(02)00094-3 [3] Kipper M., Marcoux M., Andretta I., and Pomar C. (2018). Repeatability and reproducibility of measurements obtained by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry on pig carcasses. Journal of Animal Science, 96(5), 2027-2037. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skx046 " | Accuracy of predicting chemical body composition of growing pigs using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry | Claudia Kasper, Patrick Schlegel, Isabel Ruiz-Ascacibar, Peter Stoll, Giuseppe Bee | <p>Studies in animal science assessing nutrient and energy efficiency or determining nutrient requirements necessitate gathering exact measurements of body composition or body nutrient contents. Wet chemical analysis methods or standardized dissec... |  | Agricultural sustainability, Animal nutrition modelling, Monogastrics, Physiology, Pig nutrition | Florence Gondret | 2020-09-17 10:44:58 | View | |
24 Mar 2023
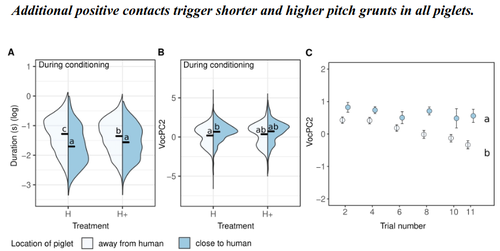
The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationshipAvelyne S Villain, Carole Guérin, Céline Tallet https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.15.484457Qualitative aspects of grunts vary with pigs' mental statesRecommended by Isabelle Veissier based on reviews by Matteo Chincarini and 1 anonymous reviewerVillain et al., (2023) investigated the structure of vocalisations in piglets in relation to human-animal-relationship. They first established a positive relationship by habituating piglets to be positively handled at weaning or later on after weaning. They then compared the reactions of piglets previously positively handled at weaning to that of non-handled piglets during tests in presence of a human (interacting or not), and also before and after the conditioning period when all piglets received positive contacts. They showed that the duration and frequency of grunts emitted in the presence of the human depends on previous contacts. More specifically, grunts are shorter and higher pitched in pigs that have been positively handled, in line with a positive human-animal relationship which is also observed through proximity of the piglets with the human. The authors concluded that the structure of pig vocalisation can reflect the quality of their relationship with humans. The authors also showed that not only the response to humans is modified by positive contacts but also the general mood of piglets, with piglets positively handled at weaning emitting shorter grunts than non-handled piglets, whatever the context. Another interesting finding is the temporality of behaviour of pigs habituated to positive contacts: during the first tests, they stay close to the human, probably being reassured by the proximity of the human. Then, when tests are repeated, they explore more the test room, using the human as an exploratory basis as already reported in the literature. The hypotheses of the study are clear. The methods are reported in details so that the work is reproducible. The interpretation of results is sound. The manuscript is clearly written. This paper brings new and original knowledge in the field of animals’ emotional responses and human-animal relationship: on the structure of grunts in relation to positive affects (positive emotion, positive mood) and on the temporality of the responses to human presence. I recommend this manuscript for its originality and quality. Isabelle Veissier Villain, A.S., Guérin, C., Tallet, C., 2023. The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationship. bioRxiv 2022.03.15.484457, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.15.484457 | The use of pigs vocalisation structure to assess the quality of human-pig relationship | Avelyne S Villain, Carole Guérin, Céline Tallet | <p>Studying human-animal interactions in domestic species and how they affect the establishment of a positive Human-Animal Relationship (HAR) may help us improve animal welfare and better understand the evolution of interspecific interactions asso... |  | Animal behaviour , Animal cognition, Animal welfare | Isabelle Veissier | 2022-03-23 09:34:45 | View | |
23 Aug 2023
Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution?Birte L. Nielsen, Huw D.R. Golledge, Jen-Yun Chou, Irene Camerlink, Péter Pongrácz, Maria Camila Ceballos, Alexandra L. Whittaker and I. Anna S. Olsson https://www.doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/s6459Can a consensus be reached on the ethical review of animal experimentation for livestock species?Recommended by Hervé Acloque based on reviews by Christian Nawroth, Patrick Gonin and Leon borgdorf"Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution?" by Birte Nielsen and colleagues [1] provides food for thought on the ethical assessment of experiments involving farm animals. While regulations can provide a precise framework, they differ from country to country and do not consider several cases, mainly when the experimentation involves non- or minimally invasive manipulations. It is also the case when research projects use farmed animals that do not fall within the scope of the regulations on animal experimentation but have undergone practices that can be authorised on farms but may raise ethical questions (tail docking, live castration, tooth filing, beak trimming, dehorning). On the other hand, the heterogeneity of the criteria taken into account by the ethics committees, when they exist (and this can differ greatly from one country to another), do not necessarily correspond to the criteria of the journals, the reviewers and the bodies brought in to evaluate the research project, or to the regulations specific to each country. All these paradoxes lead the authors to propose solutions, the most straightforward and spontaneous of which is to ask ourselves questions about this issue upstream of the experimental design required to answer a given scientific question. While increasing the number of ethical review committees may be an insufficient option, the authors insist on the importance of improving committee members' training, taking into consideration jurisdictions' differences between countries and spending more time on ethics evaluation during manuscripts' reviewing. In addition, the upstream assessment of research projects by ethics committees, specific to an institution (research institute, universities, companies), a scientific publisher or even a dedicated international ethical review board may also be a good option. The ethical evaluation of research projects is a question at the heart of our research activities, for which we do not have all the answers. As with scientific reviewing, we must take on the role of evaluator or be evaluated ourselves, using criteria and feelings that are not always consensual. The heterogeneity of evaluation systems within the scientific community, the lack of training for scientists in the fundamentals of ethical evaluation, and the different perceptions of the animal condition between countries and cultures can lead to a reciprocal lack of understanding between evaluator and evaluated, and sometimes a feeling of injustice, as some research may be easy to conduct in one country but difficult in another. Indeed, it is exciting to read the exchanges between the authors and the three reviewers who assessed this opinion paper to appreciate the diversity of points of view and see specific points of divergence. In addition to animal experimentation, the judgment handed down on 30 June 2023 by the French court penalising a pig farmer for the abusive use of an authorised breeding practice (tail docking) is a perfect illustration of the fact that the ethical assessment of practices and handling of farm animals now extends far beyond the scientific world and is becoming an increasingly important factor in the relationship between society and animal breeding. Failure to consider this evolution, whether in experimentation or animal husbandry, may have legal consequences and increase the lack of understanding between our practices and how society perceives them. The questions raised and the solutions proposed in the article by Nielsen et al. are central to our concerns, not only for the scientific community but also to meet the expectations of all stakeholders. Finally, although the authors do not directly address the question of genome editing and research using edited farm animals, this is and will be at the heart of future issues concerning the ethical evaluation of research projects. As with practices and manipulations, the intentionality of the modifications induced leads us to question and evaluate, in farmed species, their consequences on animal welfare and their relevance to society and the development of more sustainable and socially accepted animal husbandry. Reference [1] Nielsen, B. L., Golledge, H. D. R., Chou, J., Camerlink, I., Pongrácz, P., Ceballos, M., Whittaker, A. L., Olsson, I. S. (2023) Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution? OSF Preprints. Ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/s6459 | Ensuring ethical animal welfare research: Are more ethics review committees the solution? | Birte L. Nielsen, Huw D.R. Golledge, Jen-Yun Chou, Irene Camerlink, Péter Pongrácz, Maria Camila Ceballos, Alexandra L. Whittaker and I. Anna S. Olsson | <p>As the article is a short Opinion Paper, it has no abstract, but it aims to highlight the inherent challenges to ethics review of animal (welfare) science research, especially the differences between different countries and jurisdictions which ... |  | Animal behaviour , Animal welfare, Open science, Veterinary science | Hervé Acloque | 2023-05-05 13:27:22 | View | |
01 Sep 2022

Detecting dairy cows' lying behaviour using noisy 3D ultrawide band positioning dataI. Adriaens, W. Ouweltjes, M. Pastell, E. Ellen, C. Kamphuis https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6627251A novel method to monitor lying behaviour of dairy cows by combining noisy spatial positioning data, time-series segmentation based on statistical changepoints and machine learning classification algorithmRecommended by Eliel Gonzalez-Garcia based on reviews by Kareemah Chopra and John Fredy Ramirez AgudeloUsing on-farm sensors in dairy farming is known to help decision makings and farmer objectives in the monitoring and potential improvement of animal behaviour, health and production performance. However, in indoor positioning systems, data interpretation is complicated by the inaccuracy and noise in the time series, missing data caused not only by sensor failure or the harsh and changing farm environments in which they operate, but also by the animals' specific physiology itself. Thus, working with spatial data has proven challenging mainly due to their enormous heteroscedasticity, which depends on multiple factors such as the cow, the time of the day, the behaviour, factors interfering with the sensor system, etc., for which we cannot account mathematically. Applying purely black-box approaches generally results in insufficient robustness, interpretability and generalisability. With this work, Adriaens et al. (2022) developed a relatively simple and new methodology to monitor the lying behaviour of dairy cows by using noisy spatial positioning data, while combining time-series segmentation based on statistical changepoints and a machine learning classification algorithm. The two-step methodology identifies lying behaviour using an ultra-wide band indoor positioning system. Getting-up or lying-down events were indicated by the accelerometers. Overall classification and lying behaviour prediction performance was above 91% in independent test sets, with a very high consistency across cow-days. The robustness of the algorithm was demonstrated by the fact that both the cow identity-based split and the time-based split performed equally well. The article represents an original contribution for advancing the state of the art in the automated quantification of lying behaviour in dairy cows, aiming to monitor health or animal welfare issues. Future research must be considered however to validate the performance of the model when using different position-measuring technologies, in other farm settings and over a longer period of time.
Reference Adriaens I, Ouweltjes W, Pastell M, Ellen E, Kamphuis C. 2022. Detecting dairy cows' lying behaviour using noisy 3D ultra-wide band positioning data. Zenodo, 6627251, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6627251
| Detecting dairy cows' lying behaviour using noisy 3D ultrawide band positioning data | I. Adriaens, W. Ouweltjes, M. Pastell, E. Ellen, C. Kamphuis | <p>In precision livestock farming, technology-based solutions are used to monitor and manage<br>livestock and support decisions based on on-farm available data. In this study, we developed<br>a methodology to monitor the lying behaviour of dairy c... |  | Animal behaviour , Mathematical modelling, Precision livestock farming | Eliel Gonzalez-Garcia | 2022-02-28 18:19:37 | View | |
09 Feb 2024
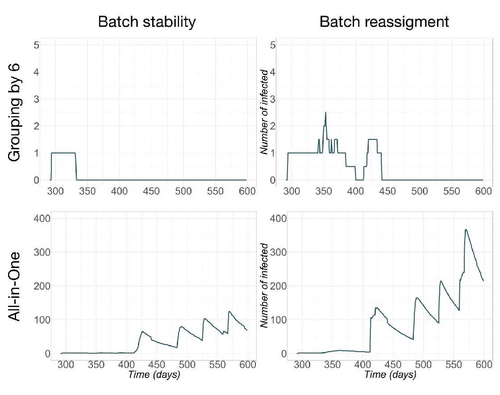
Pig herd management and infection transmission dynamics: a challenge for modellers.Vianney Sicard, Sébastien Picault, Mathieu Andraud https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.17.541128Towards models of infection transmission dynamicsRecommended by Marie-Pierre Letourneau Montminy based on reviews by Gustavo Machado and 1 anonymous reviewerEpidemics such as PRRSv-like virus in pig farms has tremendous impact on the competitiveness of swine production. However, its control requires an understanding of the complex interaction between pathogen transmission, disease impact, population dynamics and management. By using mechanistic epidemiological modelling, Sicard et al. (2023) open up a very interesting field of possibilities. This article describes work aimed at assessing the consequences of infections, taking into account the interaction between clinical outcomes and population dynamics. This study shows how this interaction can influence transmission dynamics at the herd level. It highlights the need to further explore this direction, integrating both disease impacts in breeding practices and structural changes in population dynamics, such as pig crossbreeding and grouping methodologies. Reference Sicard V, Picault S, Andraud M (2023) Pig herd management and infection transmission dynamics: a challenge for modellers. bioRxiv, 2023.05.17.541128. ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.17.541128
| Pig herd management and infection transmission dynamics: a challenge for modellers. | Vianney Sicard, Sébastien Picault, Mathieu Andraud | <p>The control of epidemics requires a thorough understanding of the complex interactions between pathogen transmission, disease impact, and population dynamics and management. Mechanistic epidemiological modelling is an effective way to address t... |  | Animal epidemiology modelling, Animal health, Bioinformatics, Farming systems, Infectious diseases, Mathematical modelling, Open science, Population dynamics, Veterinary epidemiology | Marie-Pierre Letourneau Montminy | 2023-05-22 15:07:37 | View | |
29 Jan 2024
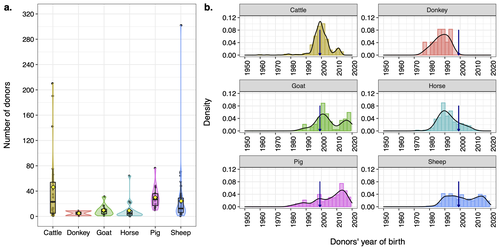
Assessing the potential of germplasm collections for the management of genetic diversity: the case of the French National CryobankAlicia Jacques, Delphine Duclos, Coralie Danchin-Burge, Marie-Jose Mercat, Michele Tixier-Boichard, Gwendal Restoux https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.19.549644Exploring Genetic Diversity Management: Unveiling the Potential of Germplasm Collections in the French National CryobankRecommended by Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas based on reviews by Roy Costilla and 1 anonymous reviewerThe study by Jacques et al. (2024) addresses a critical concern in the context of genetic diversity erosion in domesticated animal populations. The research uses data from the cryopreserved resources from the French National Cryobank to manage genetic diversity in livestock species. The authors employ a comprehensive methodology to propose novel biodiversity metrics to characterize the status of genetic diversity of cryopreserved collections including cattle, sheep, goat, horse, donkey, and pig livestock species. The findings reveal significant variations of genetic diversity at species and breed levels. Breeds with a large commercial distribution had more donors in the collection than local breeds. The authors propose a practical framework for assessing germplasm collections, providing a valuable tool for planning and managing collections at both national and international levels. The study also highlights the usefulness of the Gini-Simpson and effective donor numbers indices to plan a more efficient sampling, whereas the index of diversity impact can be employed in the selection of the most suitable donors for immediate use, based on pedigree but also using genetic markers. In resume, this study makes a significant contribution to the field by offering a framework for the assessment of germplasm collections. Its innovative metrics provide insights that could guide strategic decision-making in planning, managing, and utilizing cryopreserved resources. This research is relevant and can benefit conservationists, and population genetics working towards the preservation and sustainable use of genetic resources in livestock species. Reference Jacques, A., Duclos, D., Danchin-Burge, C., Mercat, M. J., Tixier-Boichard M., Restoux, G. (2024). Assessing the potential of germplasm collections for the management of genetic diversity: the case of the French National Cryobank. bioRxiv 2023.07.19.549644. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.19.549644
| Assessing the potential of germplasm collections for the management of genetic diversity: the case of the French National Cryobank | Alicia Jacques, Delphine Duclos, Coralie Danchin-Burge, Marie-Jose Mercat, Michele Tixier-Boichard, Gwendal Restoux | <p>Through a combination of selective pressure and genetic drift, there has been a notable erosion of genetic diversity in domesticated animal populations. In response, many countries, including France, have developed gene banks in order to conser... |  | Animal genetics | Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas | 2023-07-20 19:08:40 | View | |
20 Dec 2021

Quantifying growth perturbations over the fattening period in swine via mathematical modellingManuel Revilla, Guillaume Lenoir, Loïc Flatres-Grall, Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo, Nicolas C Friggens https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.22.349985An innovative modelling approach to enhance the quality of the quantification of pig resilience during the entire fattening period: Towards an individual pig resilience indexRecommended by Mohammed Gagaoua based on reviews by Arata Hidano, Ludovic Brossard and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Arata Hidano, Ludovic Brossard and 2 anonymous reviewers
The identification of reliable estimates of growth potential and resilience over the fattening period in large populations is a challenge in actual swine breeding conditions. To overcome this drawback, the study by Revilla et al. 2021 in the frame of precision livestock farming aimed to propose an innovative modelling approach, in addition to previous studies from the same group (Revilla et al. 2019), to enhance the quality of the quantification of pig resilience during the entire fattening period. The authors developed a model that quantifies an “individual pig resilience indicator” based on longitudinal data, for instance body weight, recorded routinely by a commercially available automatic feeding system. Revilla and co-workers considered in their study two mainly commercialised pure pig breeds these being Piétrain including Piétrain Français NN Axiom line (Pie NN) free from halothane-sensitivity (ryanodine receptor gene, RYR1) and Piétrain Français Axiom line positive to this gene and Duroc. Therefore, the authors investigated the potential of improving resilience of swine livestock through inclusion for the first time of an “individual pig resilience indicator” in breeding objectives. A database of 13 093 boars (approximately 11.1 million of weightings) belonging to Pie (n= 5 841), Pie NN (n = 5 032) and Duroc (n= 2 220) finished under ad libitum feeding, high sanitary level and controlled temperature was used to develop robust models. The authors checked the three datasets (for each pig breed) independently to explore the variation and gaps (a data pre-treatment procedure) to ensure high quality data for the modelling approach. Then, they applied the Gompertz model and linear interpolation on body weight data to quantify individual deviations from the expected production, allowing the creation of the ABC index. For the modelling, the authors applied a two-step mathematical model approach by first establishing a theoretical growth curve of each animal, while the second step aimed to build the actual perturbed growth curve. The heritability of the index ranged from 0.03 to 0.04, with similar heritability between Piétrain and Duroc breeds. Moreover, moderate genetic relationships were computed between the proposed index and important phenotypic traits in swine production likely BF100: backfat thickness at 100kg; LD100: longissimus dorsi thickness at 100kg; ADG: average daily gain during control and FCR: feed conversion ratio. Developing models able to capture perturbations during the fattening period is a challenge in swine breeding industry. The model and methodology proposed by the authors in this innovative work (although preliminary and with low heritabilities) would help overcome such limit and facilitate a real implementation at large scale in pig breeding system. The modelling approach further offers an opportunity to develop a selection criterion to improve resilience in swine breeding conditions. To explore the full potential of this modelling approach, a larger database and other factors such as breed, behaviour and feeding behaviour of the animals, rearing practices, management and environment conditions, age… etc. are worthy to consider. In the future, more in depth measurements of behaviour that can be computed for example using computer vision should be desirable to increase the robustness of the proposed model. References Revilla, M., Friggens, N.C., Broudiscou, L.P., Lemonnier, G., Blanc, F., Ravon, L., Mercat, M.J., Billon, Y., Rogel-Gaillard, C., Le Floch, N. and Estellé, J. (2019). Towards the quantitative characterisation of piglets’ robustness to weaning: a modelling approach. Animal, 13(11), 2536-2546. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731119000843 Revilla M, Lenoir G, Flatres-Grall L, Muñoz-Tamayo R, Friggens NC (2021). Quantifying growth perturbations over the fattening period in swine via mathematical modelling. bioRxiv, 2020.10.22.349985, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.22.349985 | Quantifying growth perturbations over the fattening period in swine via mathematical modelling | Manuel Revilla, Guillaume Lenoir, Loïc Flatres-Grall, Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo, Nicolas C Friggens | <p>Background: Resilience can be defined as the capacity of animals to cope with short-term perturbations in their environment and return rapidly to their pre-challenge status. In a perspective of precision livestock farming, it is key to create i... |  | Animal genetics, Animal health, Farming systems, Mathematical modelling, Precision livestock farming | Mohammed Gagaoua | 2020-10-26 11:47:08 | View | |
06 Sep 2023
Validation of a Radio frequency identification system for tracking location of laying hens in a quasi-commercial aviary systemSabine G. Gebhardt-Henrich, Alexander Kashev, Matthew B. Petelle, Michael J. Toscano https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.16.528820Tracking large numbers of hens in aviary housing: validation of a Radio Frequency Identification systemRecommended by Anna Olsson based on reviews by Arjen van Putten and Mona Giersberg based on reviews by Arjen van Putten and Mona Giersberg
With the increasing use of cage-free housing systems for laying hens comes the challenge of monitoring the behaviour of individual hens in large enclosures where they can be not only on the floors but on different levels. The aim of the present study by Gebhardt-Henrich et al., (2023) was to validate a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system with the capacity to track a large number of hens for different research and applied purposes where behaviour monitoring is relevant, such as heritability estimates for breeding programs. In a housing system with 225 birds per pens, 26 antennae were placed at different locations. All birds in 5 pens were equipped with a glass tag in a custom-developed leg band. For validation purposes, the behaviour of three hens who could move between two pens was also monitored on video. Equipping these hens with colour-coded backpacks made them identifiable on video. Matching the antennae detection of the focal birds with the behaviour observation showed that the antennae were able to detect a hen on the right tier in > 90% of cases, but that match on antenna level was lower. The limitations of the system are also discussed in this concise methods paper that will be helpful to many researchers interested in tracking laying hens in loose housing systems. Gebhardt-Henrich, S.G., Kashev, A., Petelle, M.B., Toscano, M.J., 2023. Validation of a Radio frequency identification system for tracking location of laying hens in a quasi-commercial aviary system. bioRxiv 2023.02.16.528820. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Animal Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.16.528820
| Validation of a Radio frequency identification system for tracking location of laying hens in a quasi-commercial aviary system | Sabine G. Gebhardt-Henrich, Alexander Kashev, Matthew B. Petelle, Michael J. Toscano | <p>Cage-free housing is increasingly chosen in Europe, North America, and Australia as an animal-welfare friendly farm system for laying hens. However, hens are kept in large numbers in those systems which makes checking for health and welfare dif... | Animal genetics, Animal welfare | Anna Olsson | 2023-02-17 08:54:51 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Karol B Barragán-Fonseca
Mohammed Gagaoua
Rachel Gervais
Florence Gondret
Francois Meurens
Rafael Muñoz-Tamayo
Anna Olsson
Seyed Abbas Rafat
Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas









